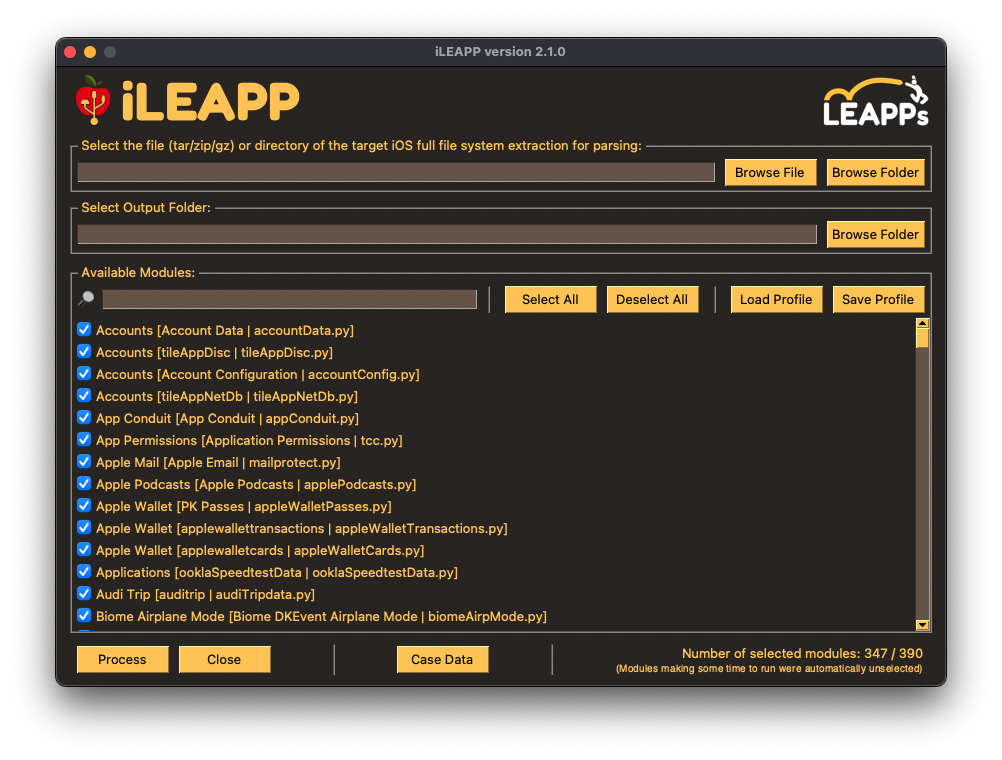
iLEAPP offers a comprehensive set of features that make it a powerful tool for iOS forensics:
- Mobile Installation Logs: Parses logs related to app installations and updates.
- iOS 12+ Notifications: Extracts and analyzes notifications from iOS 12 and later versions.
- Build Information: Retrieves detailed information about the iOS version and build.
- Wireless Cellular Service Info: Gathers data such as IMEI and phone numbers.
- Screen Icons List: Lists screen icons by their screen and grid order.
- ApplicationState.db Support: Correlates app bundle IDs with data container GUIDs.
- Connected User and Computer Names: Identifies user and computer names that the iOS device has connected to, with updates by Jack Farley (@JackFarley248, http://farleyforensics.com/).
- iLEAP Github repo: https://github.com/abrignoni/iLEAPP
iLEAPP is instrumental in various forensic scenarios, including:
- User Activity Analysis: By parsing logs and events, investigators can reconstruct user behavior and interactions with the device.
- Data Recovery: The tool can recover deleted or hidden data, contributing to more comprehensive investigations.
- Incident Response: In corporate environments, iLEAPP can assist in identifying unauthorized access or malicious activities on iOS devices.
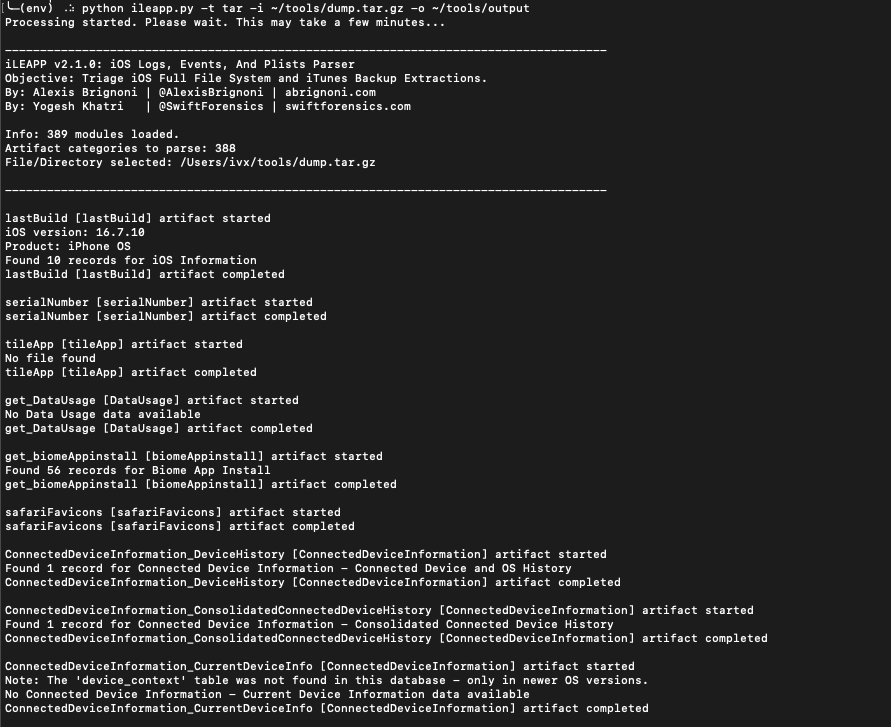
To use iLEAPP, run the following command:
Here, -t specifies the type of extraction (zip, tar, fs, or gz), -i is the path to the extraction, and -o is the path for the report output. The tool will generate a report containing the parsed data from the iOS extraction.
To run the graphical user interface (GUI) version of iLEAPP, use the following command:
To extract the full file system from an iOS device you will need a jailbroken device. Depending on how you are SSHing into the device, you can use the following command to create a tar file of the full file system:
It will take some time to create the tar file. You might notice an error "tar: Error exit delayed from previous errors" which you can ignore. Once it's done, there should be a dump.tar.gz file in your current directory on your local machine. You can then use iLEAPP to parse this file and generate a report.
Here, iLEAPP expects an existing output directory so we create one. The -t flag specifies the type of extraction (tar in this case), -i is the path to the tar file, and -o is the path for the report output. Once the command is executed, iLEAPP starts parsing the data and generates a report in the specified output directory.
Similarly, you can use the graphical interface to parse the data:
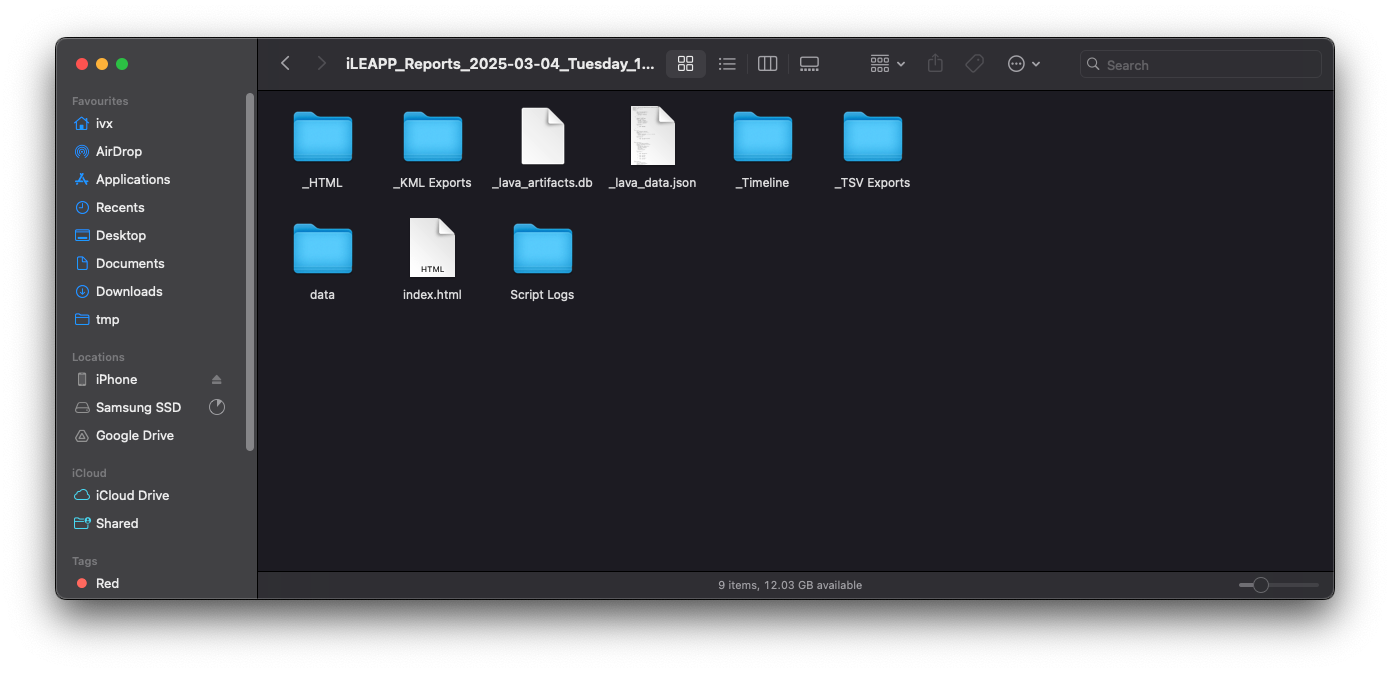
Once done, you will find the parsed data in the output directory. If you used graphical interface, you can simply click the button Open Report to view the report.
Simply open the index.html file in your browser to view the report.
The report can be navigated using the sidebar on the left, which contains various categories of parsed data. You can click on each category to view the detailed information. Here's what you can expect to find in the report:
Contains settings related to user accounts, including configurations for Apple ID and associated services.
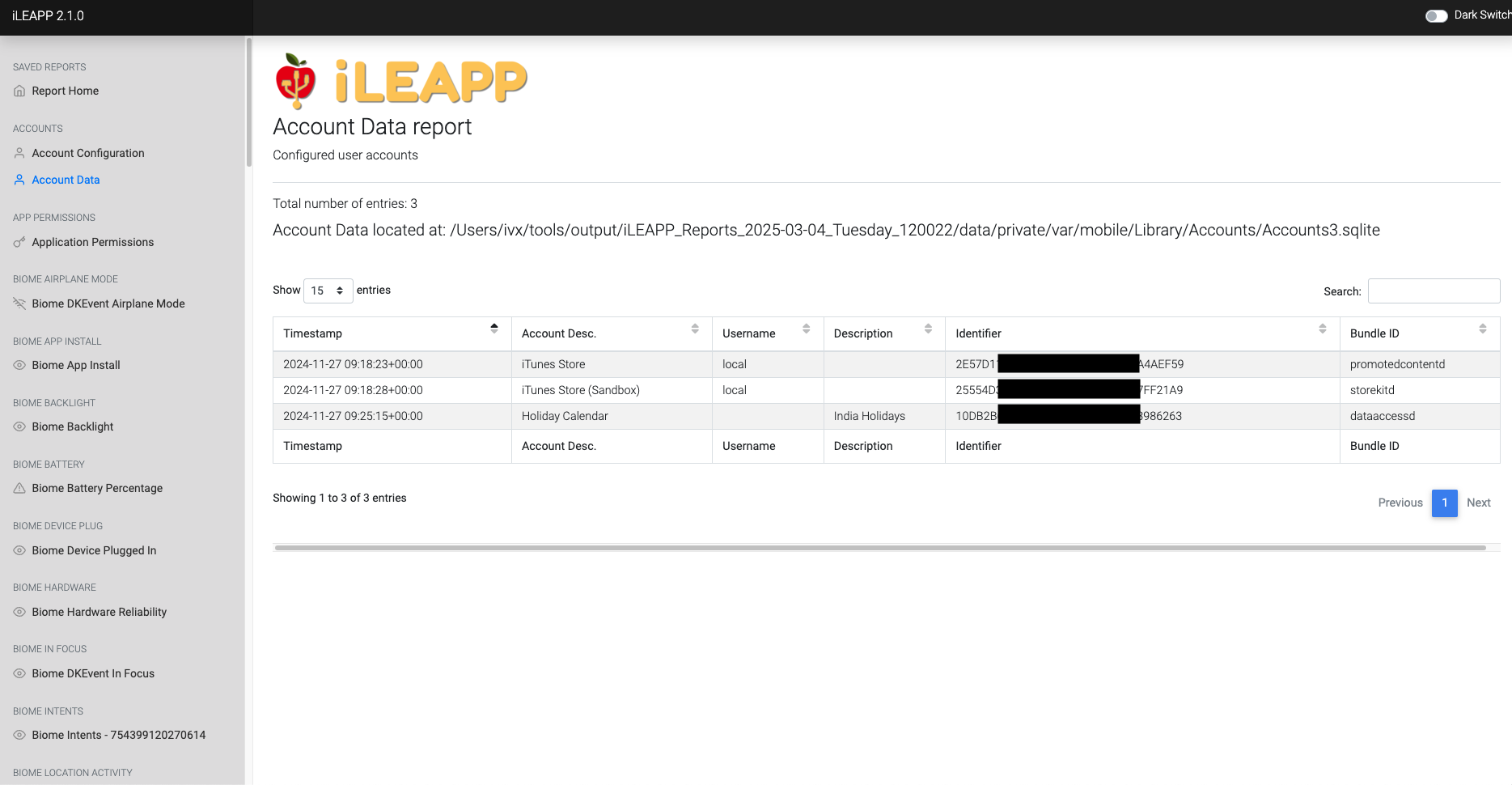
Stores detailed information about user accounts, such as linked emails, phone numbers, and associated devices.
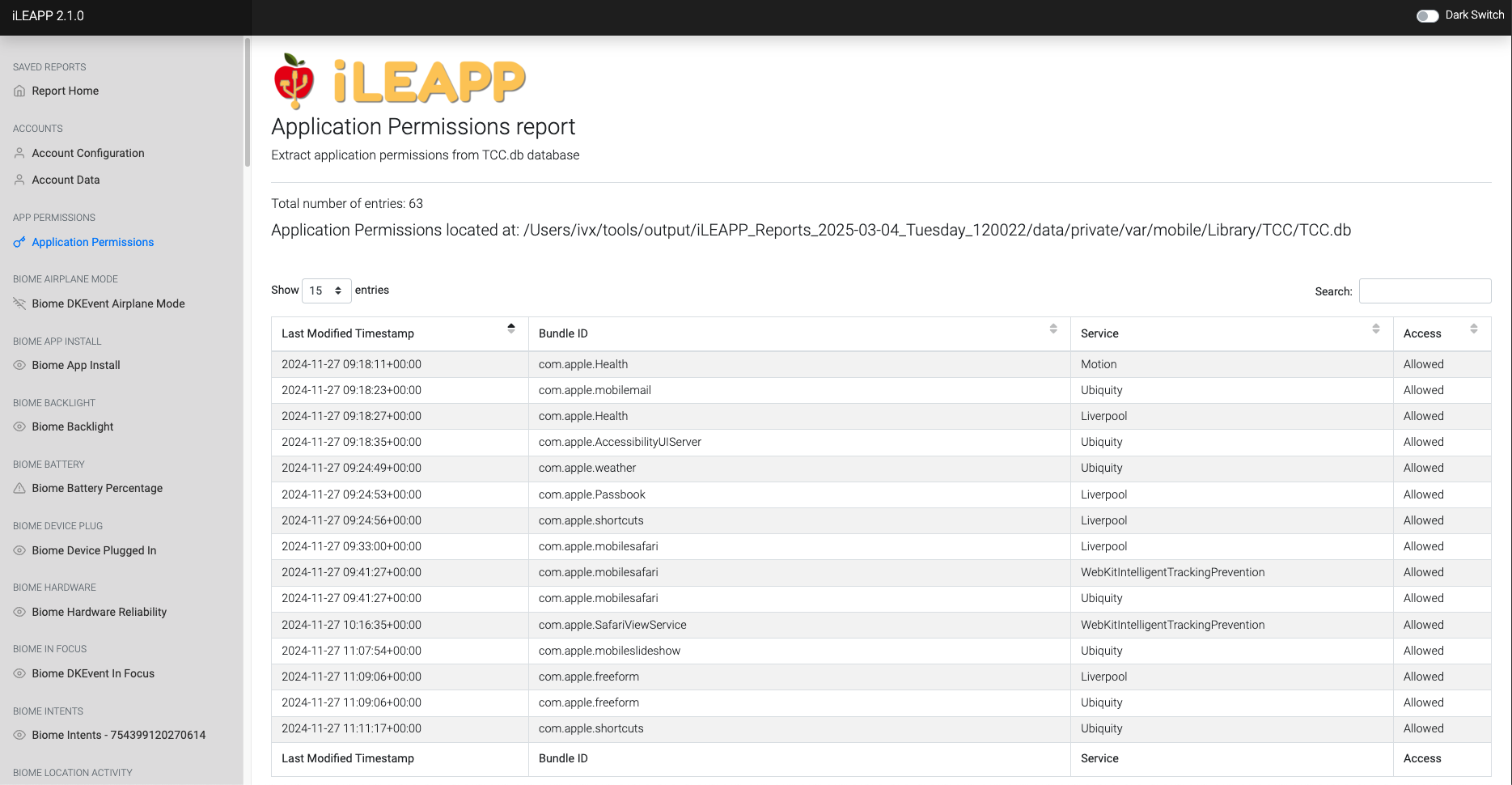
Lists permissions granted to apps, including access to location, contacts, and system features.
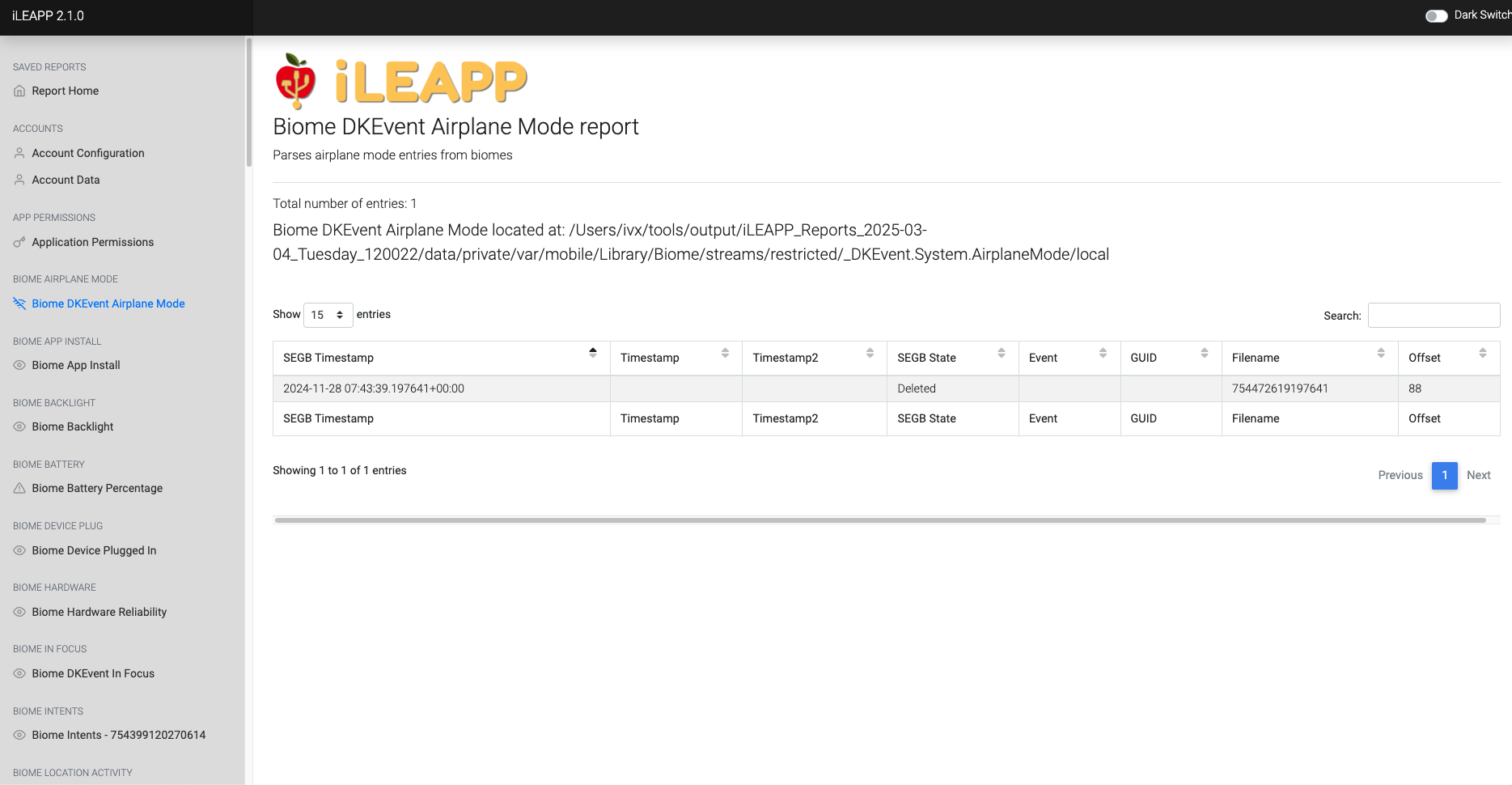
Logs instances when airplane mode is toggled on or off on the device.
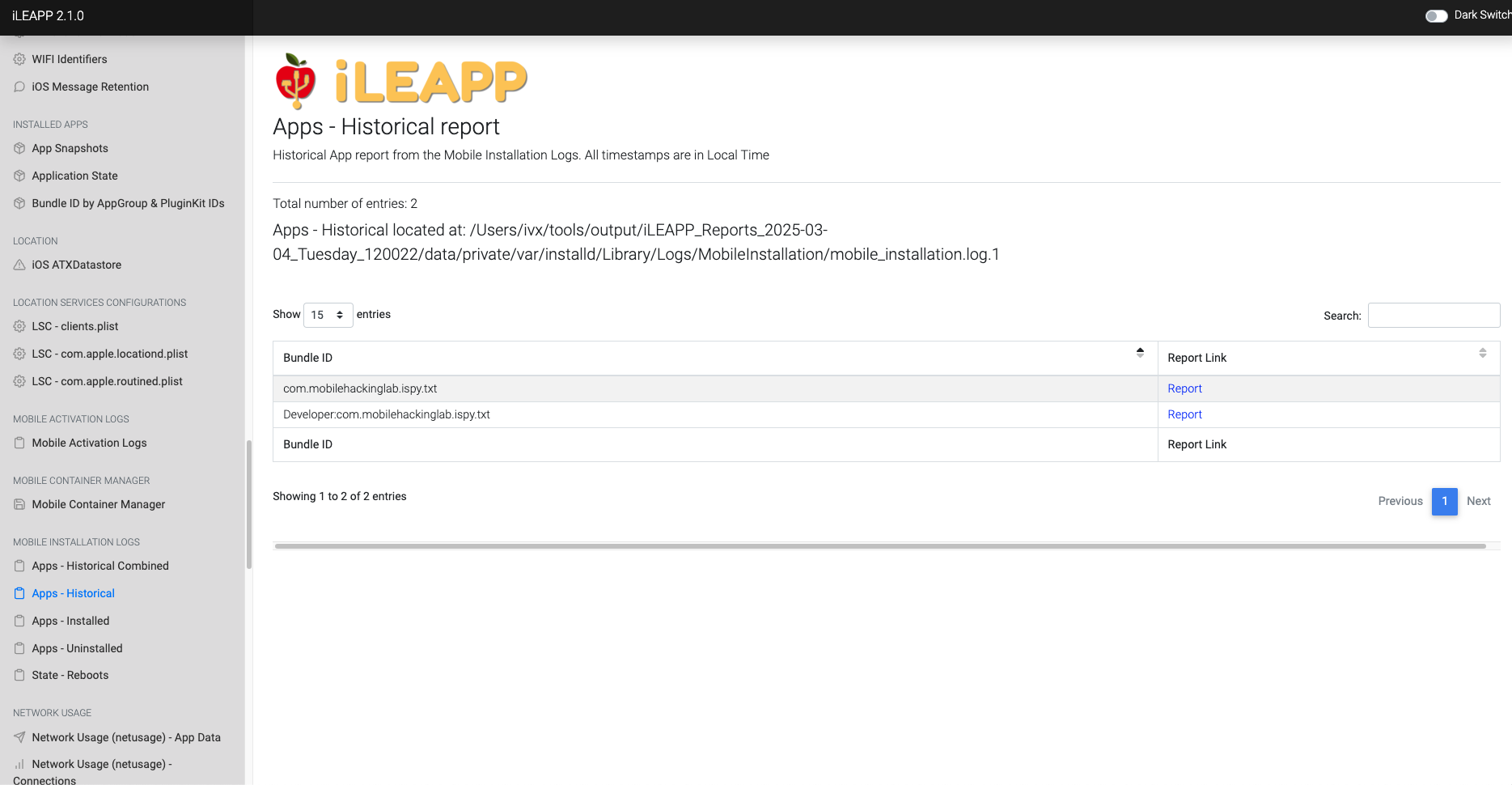
Records app installation events, including timestamps and application identifiers.
Tracks changes in screen brightness and backlight activity over time.
Logs battery percentage changes, helping analyze device power usage trends.
Records instances when the device is plugged in or unplugged from a power source.
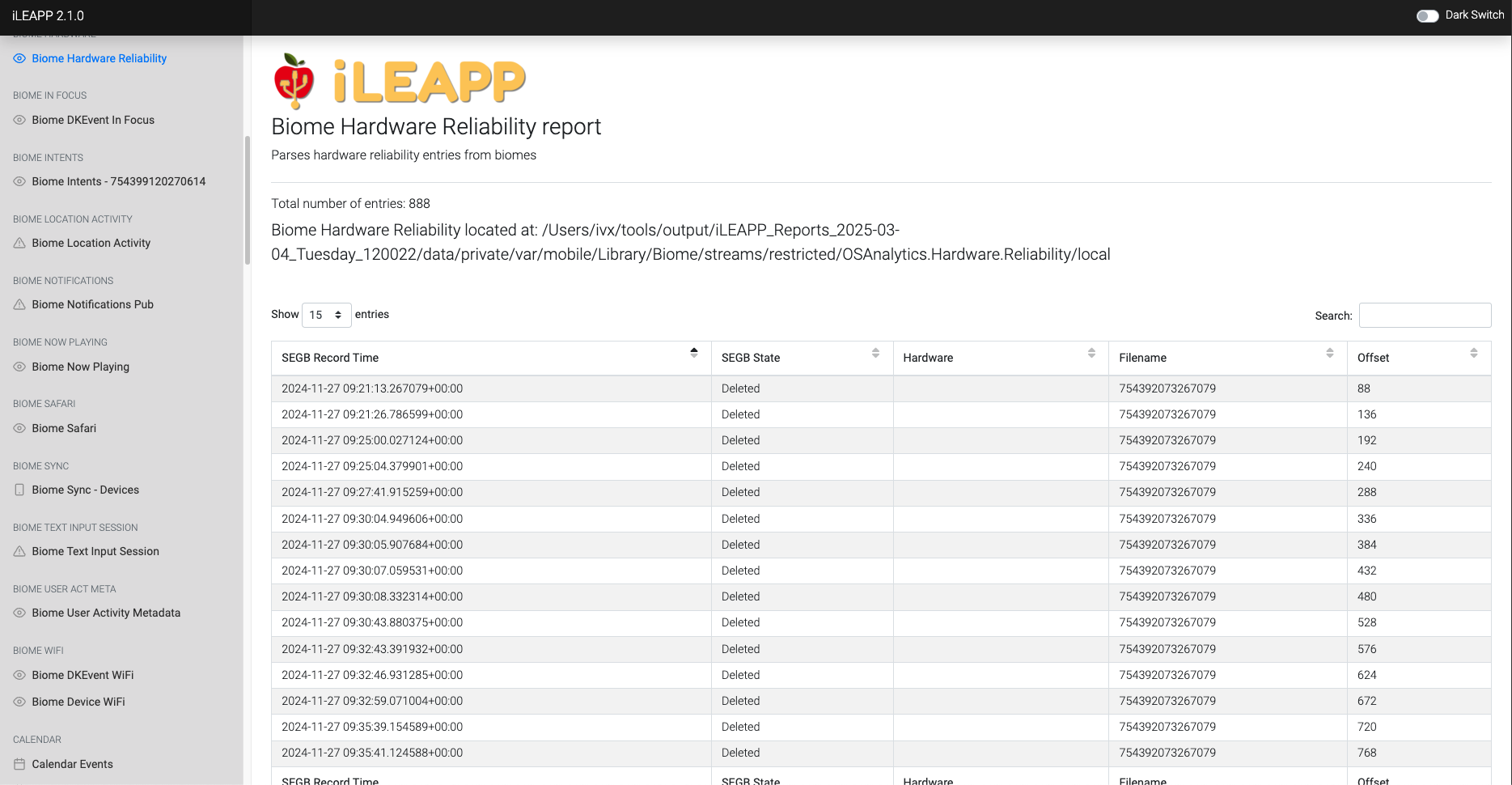
Tracks hardware-related reliability data, including component failures or issues.
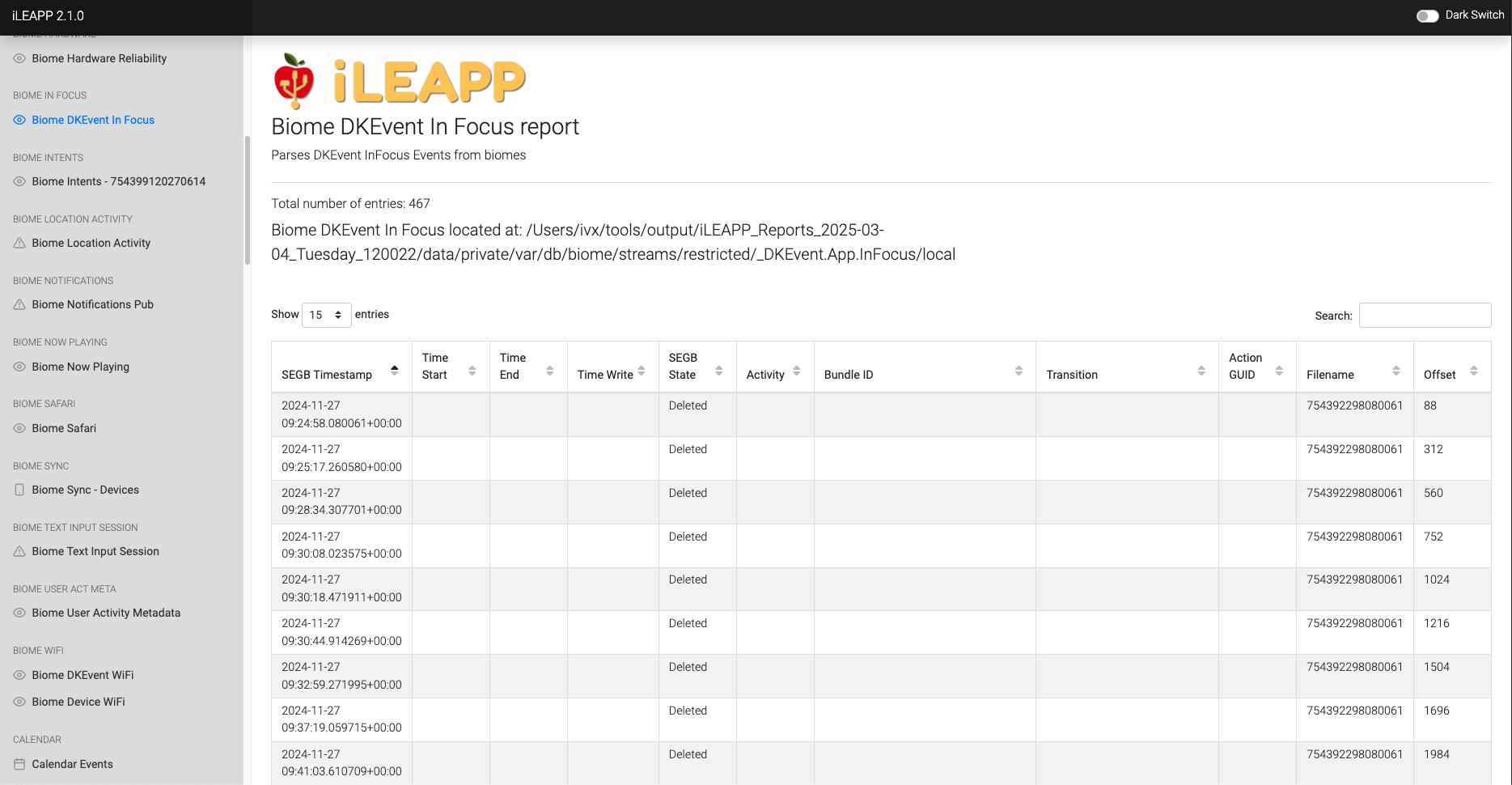
Captures information about apps that are currently in focus or being interacted with.
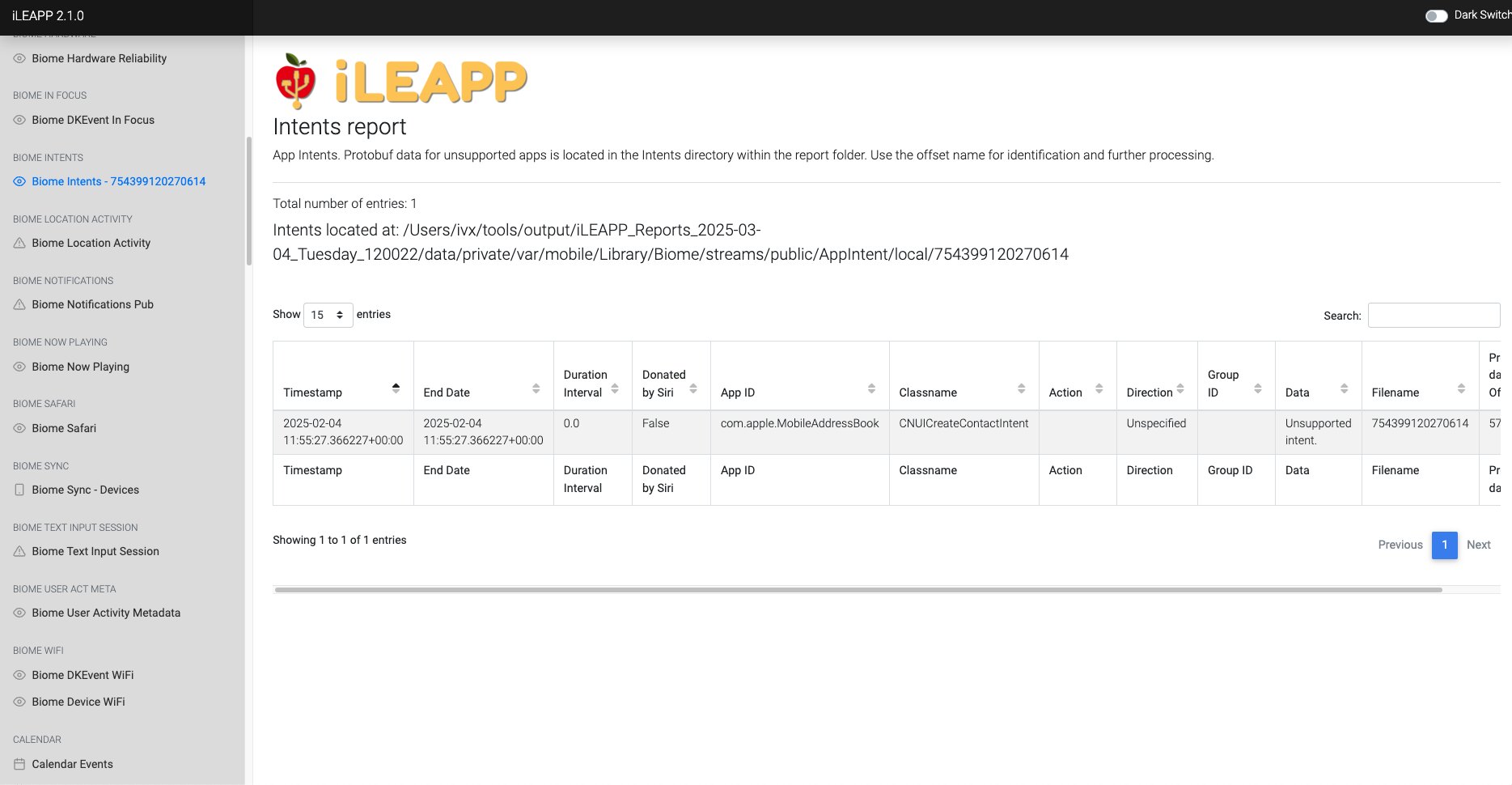
Stores system or user-initiated intents, such as opening an app or triggering an action.
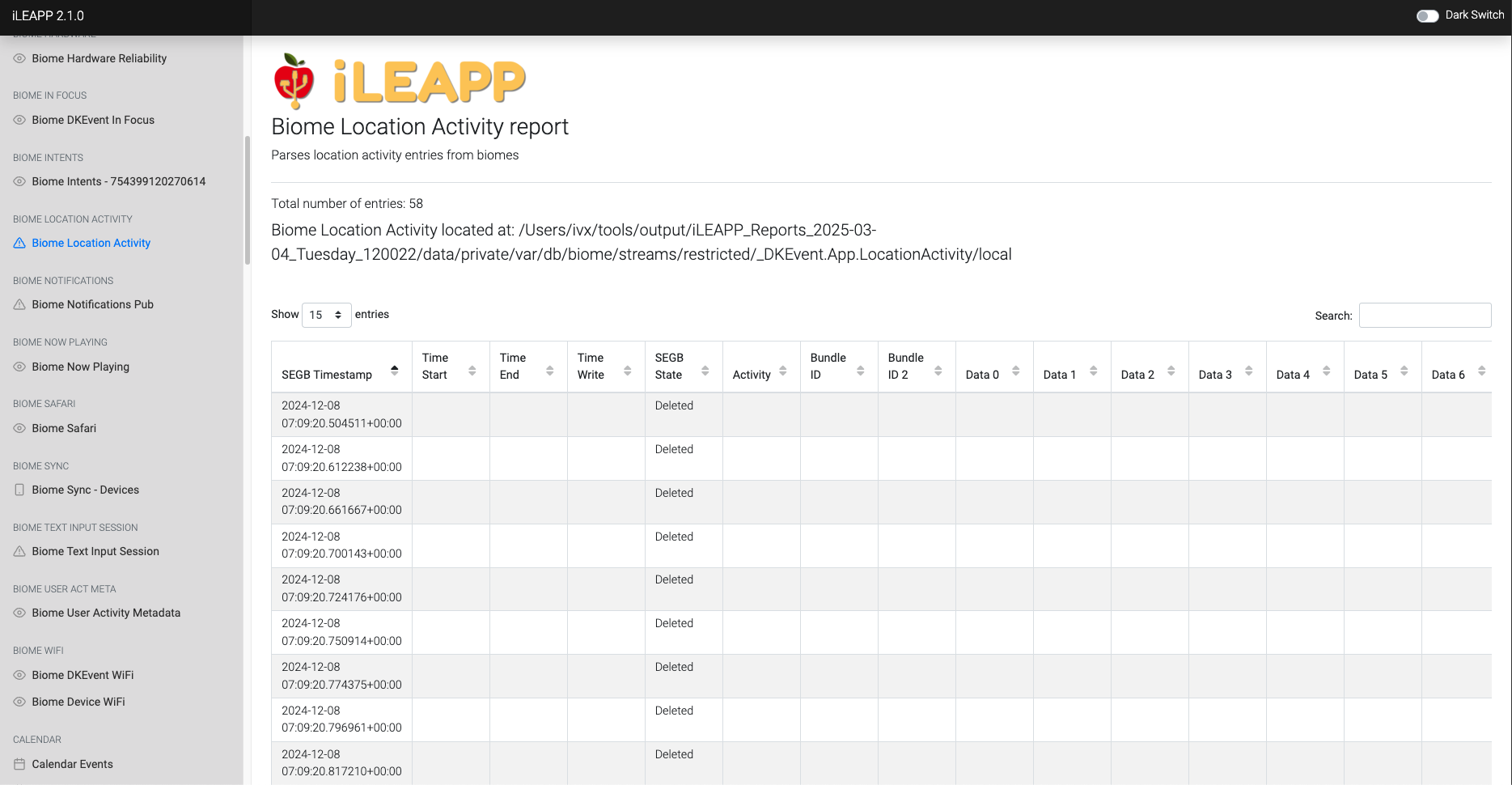
Logs movement and location-based activities detected by the system.
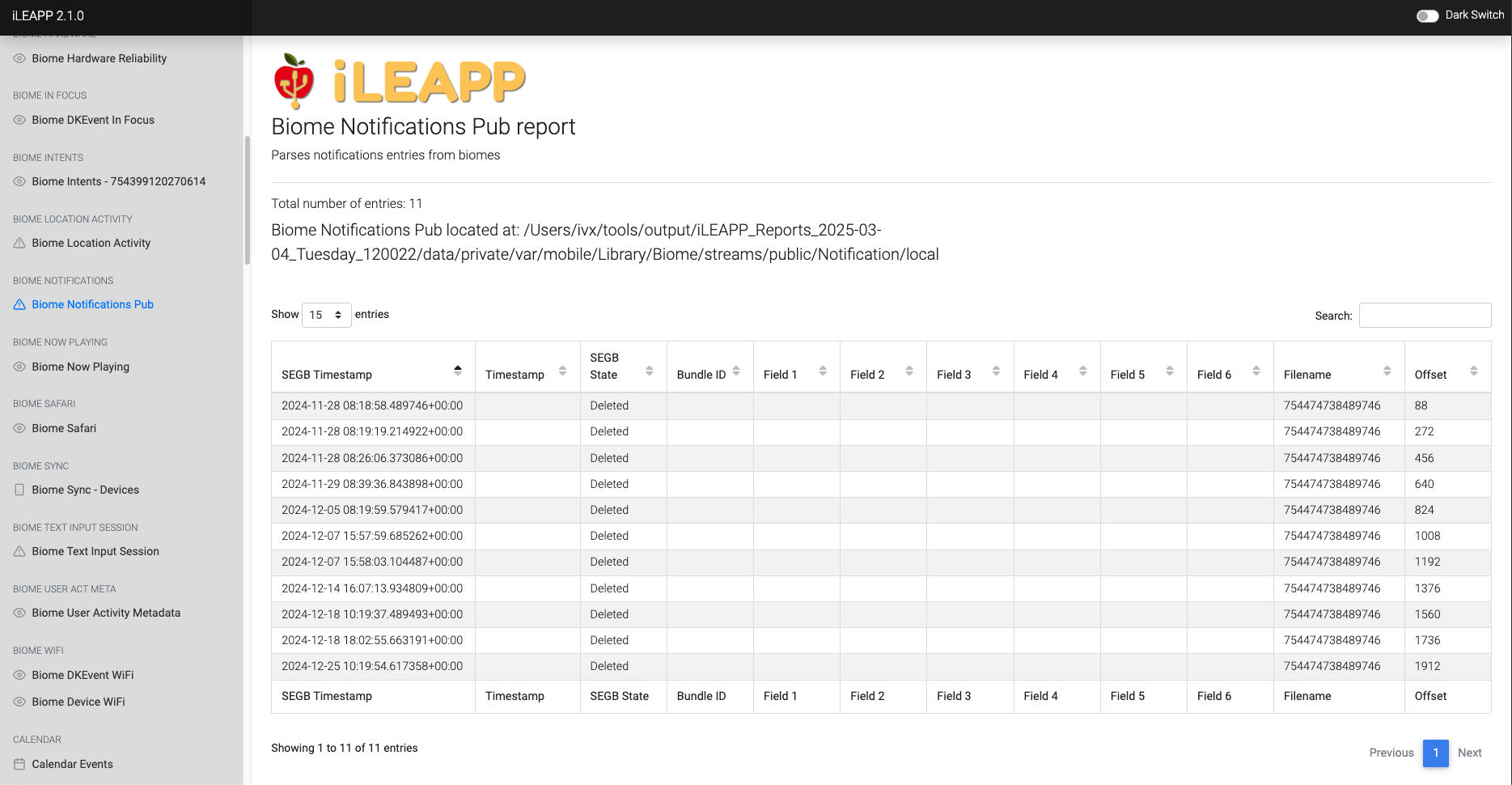
Records details about notifications received, including timestamps and app sources.
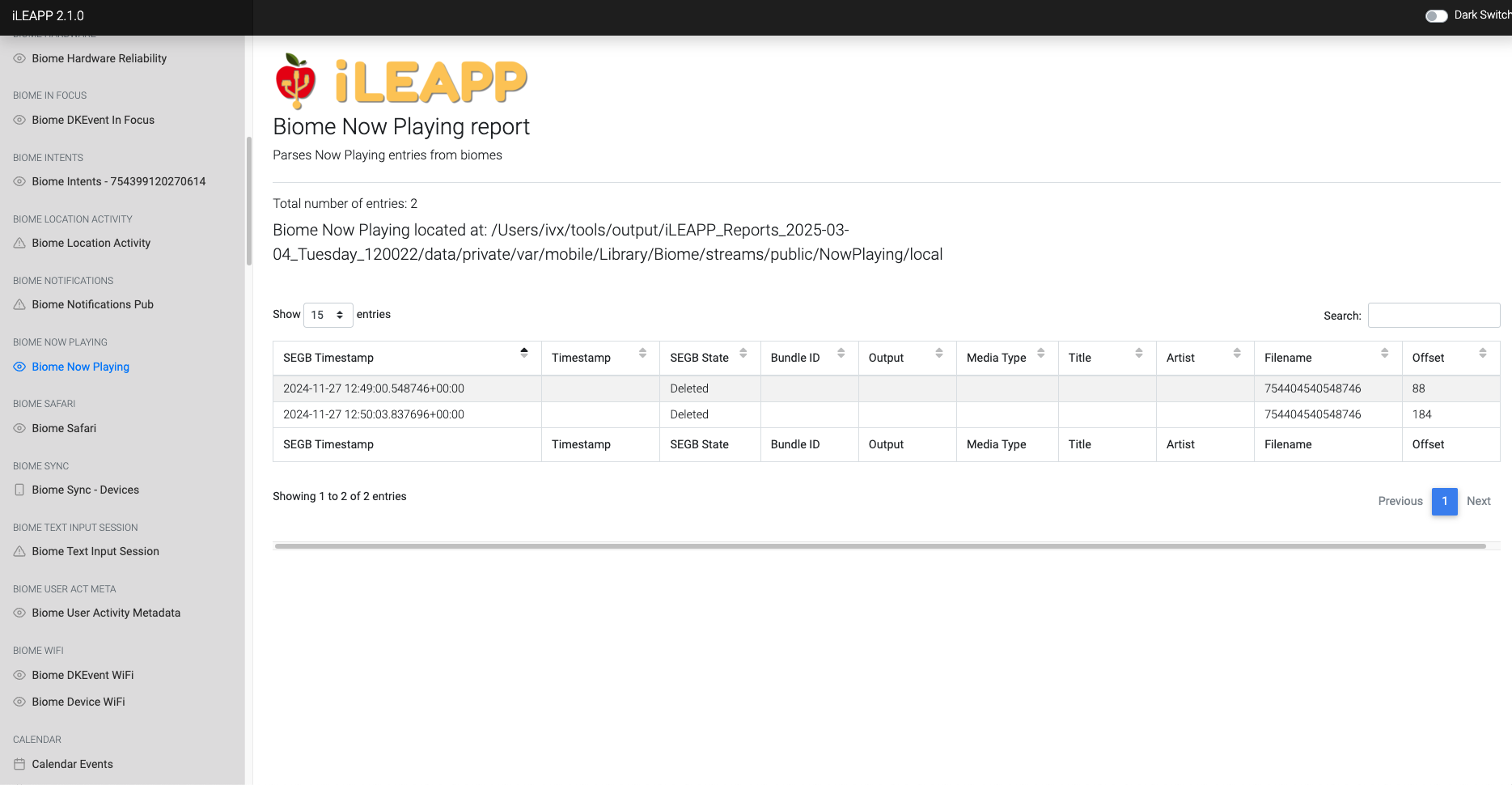
Captures information about media content currently being played on the device.
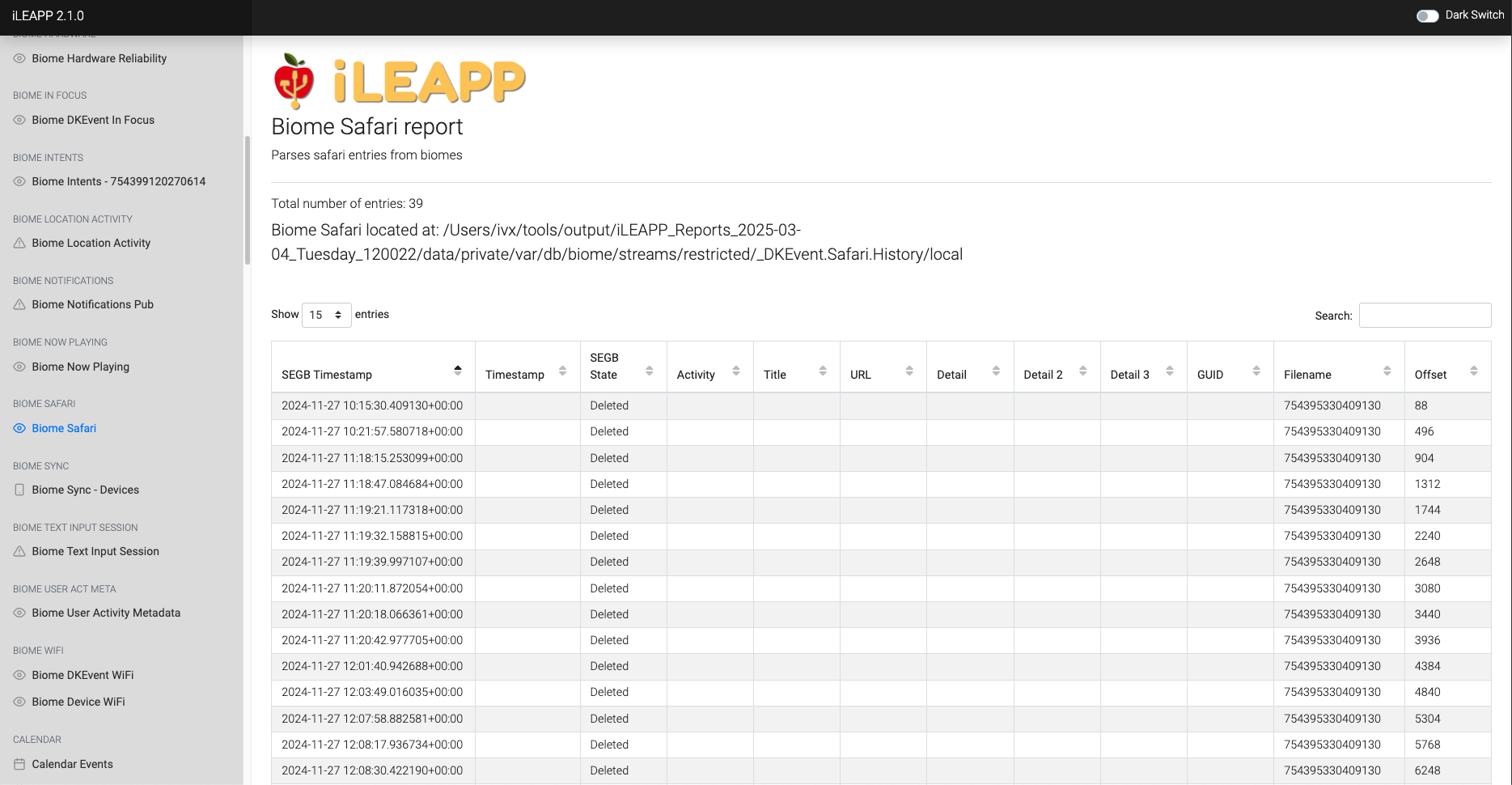
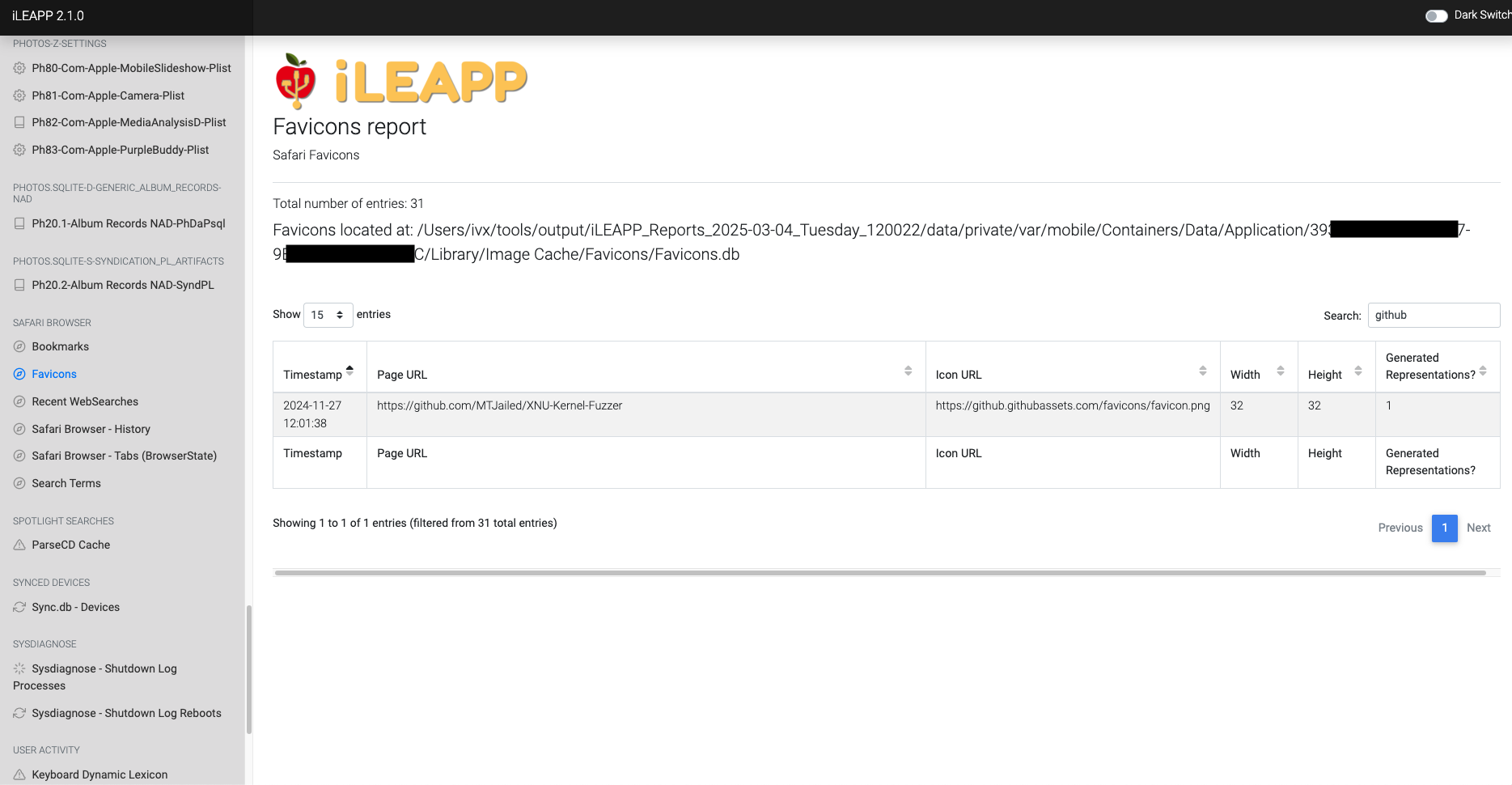
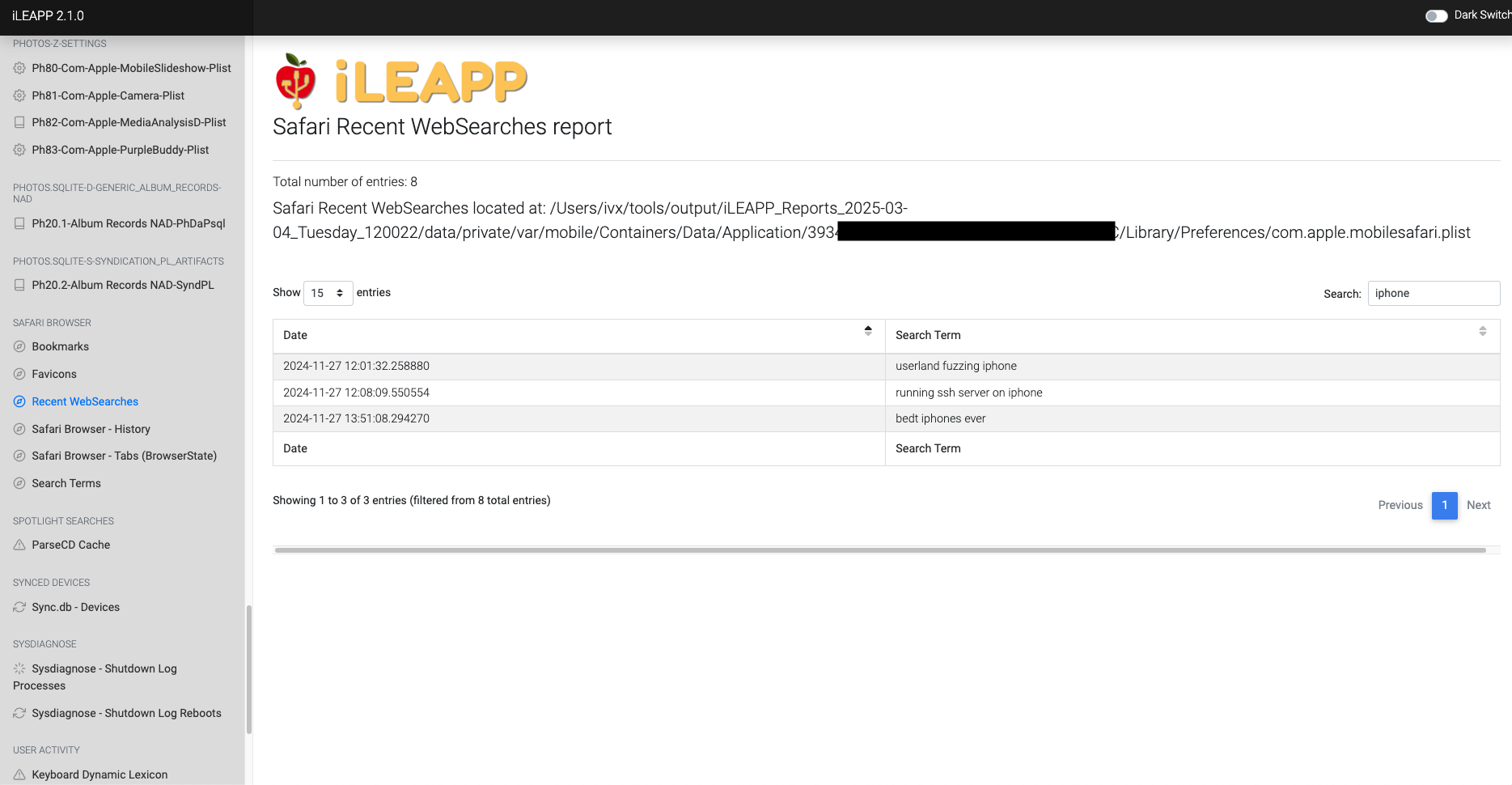
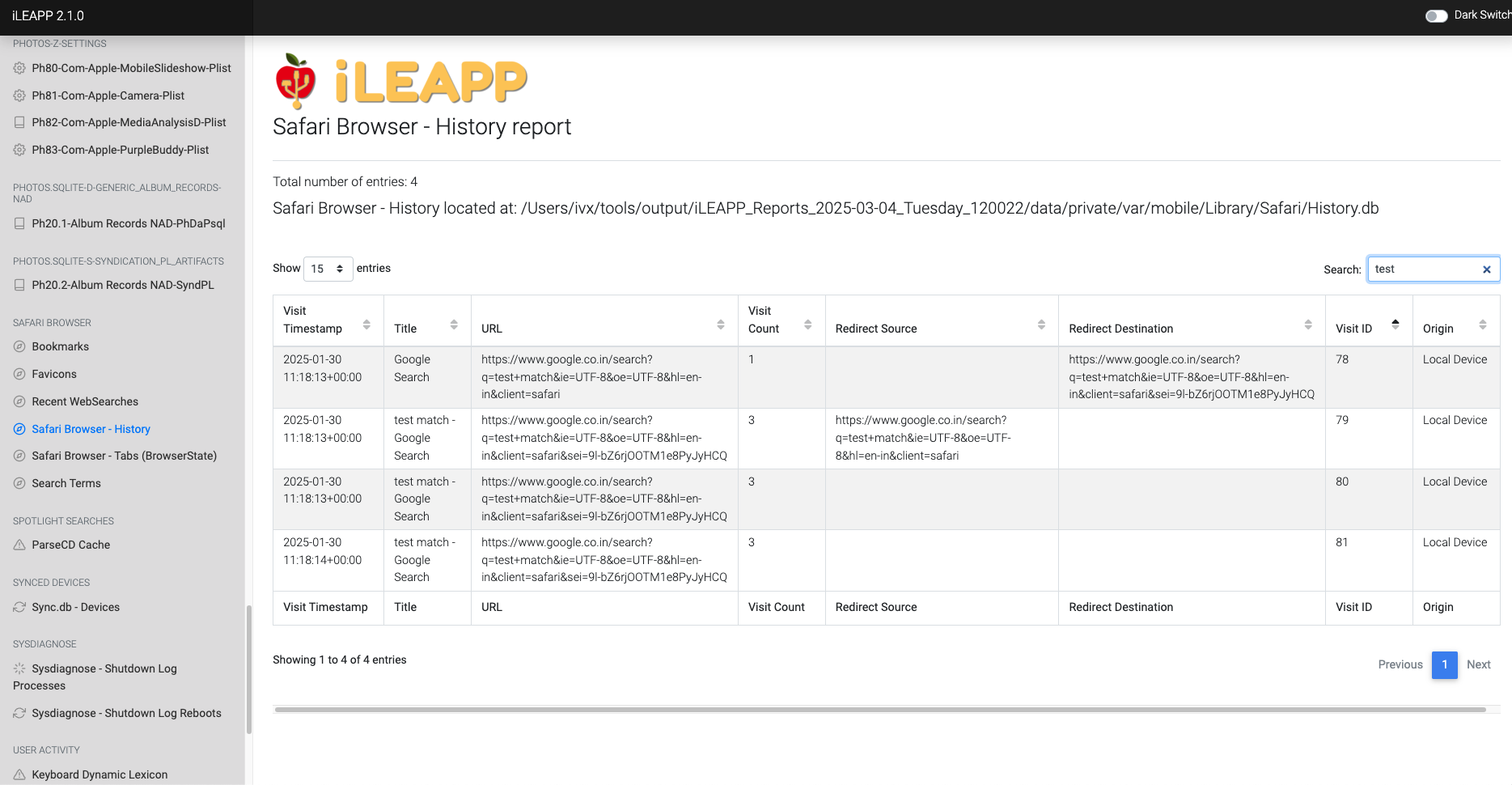
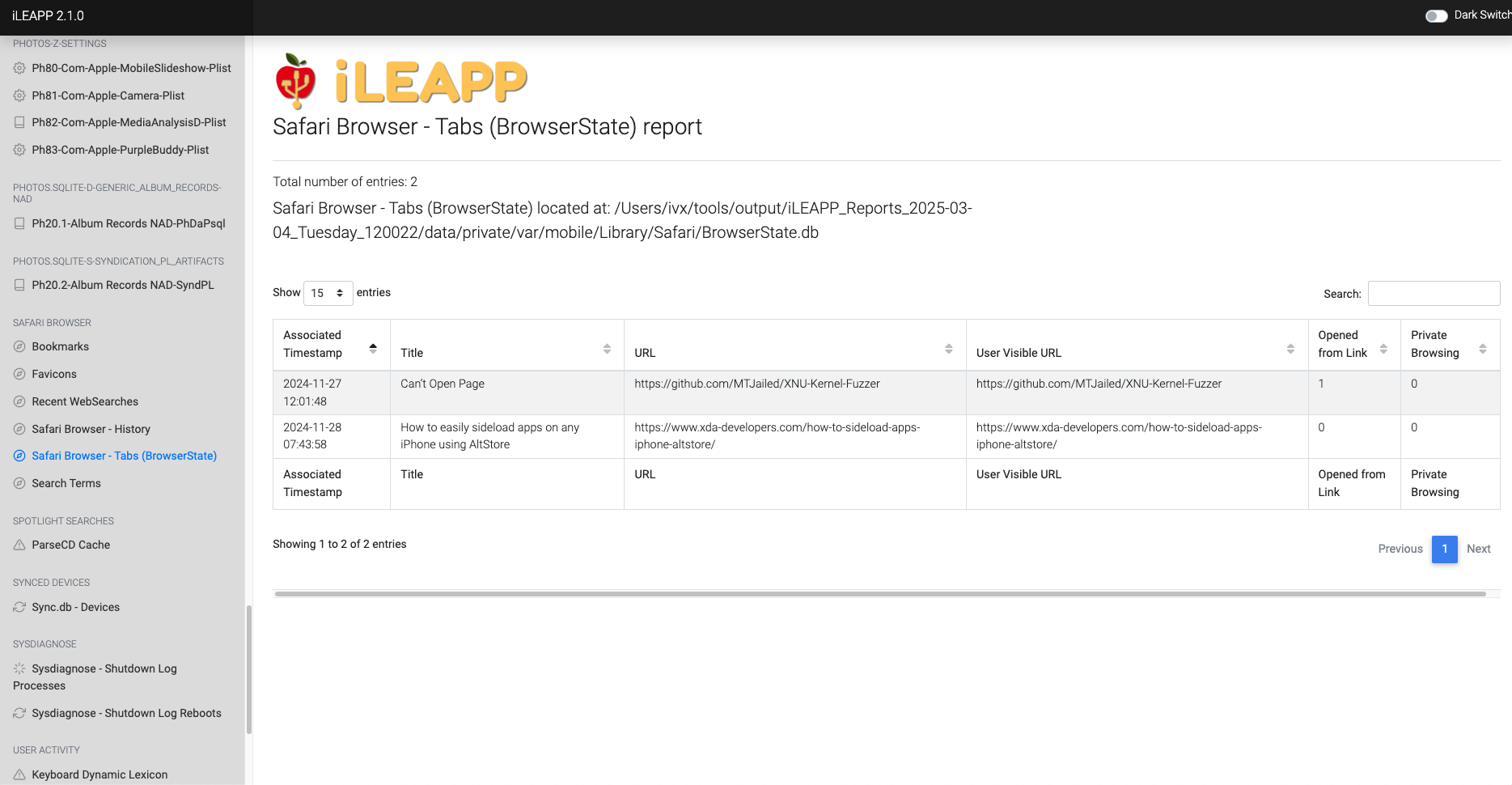
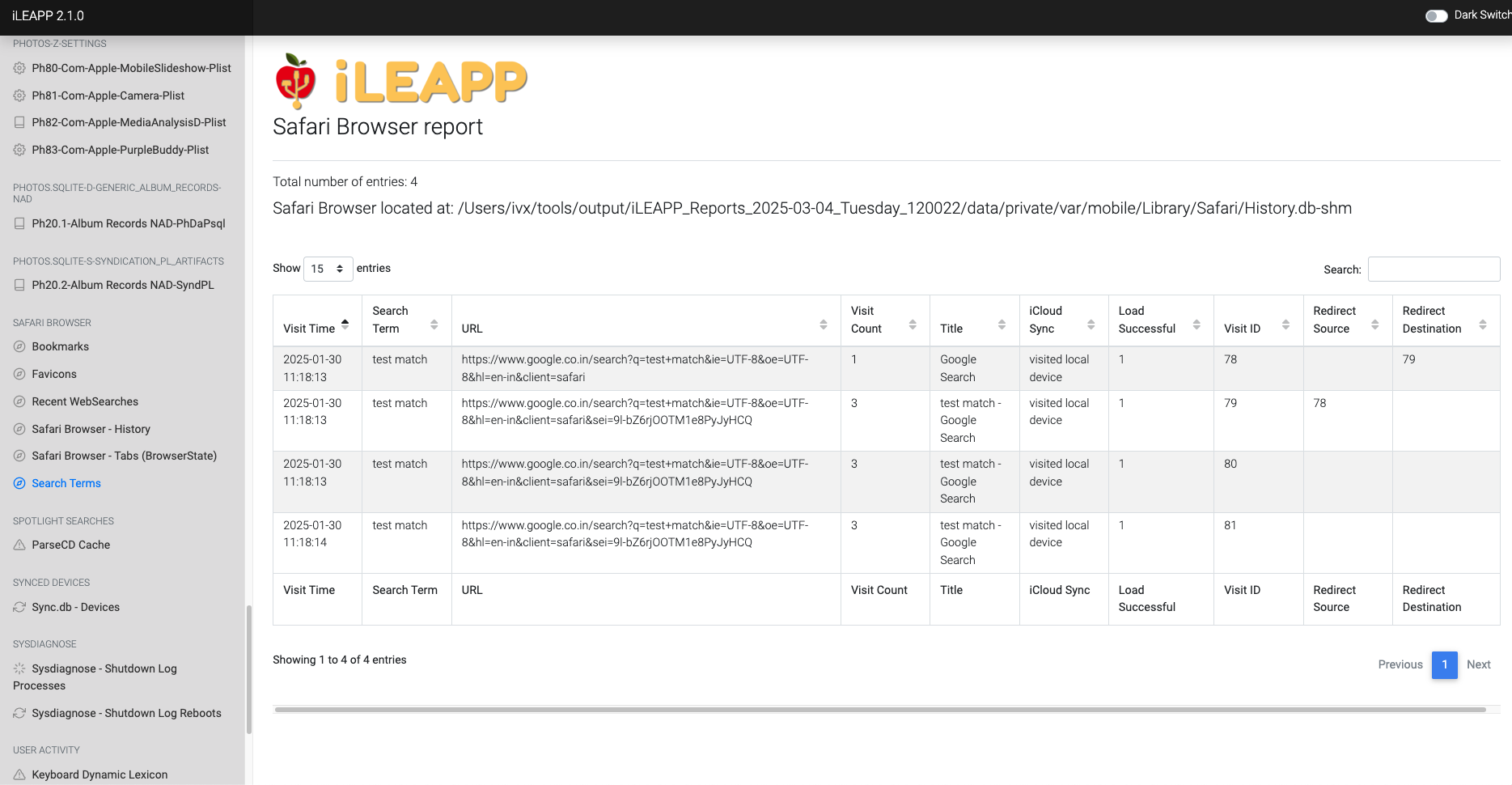
Tracks Safari browser activity, including website visits and interactions.
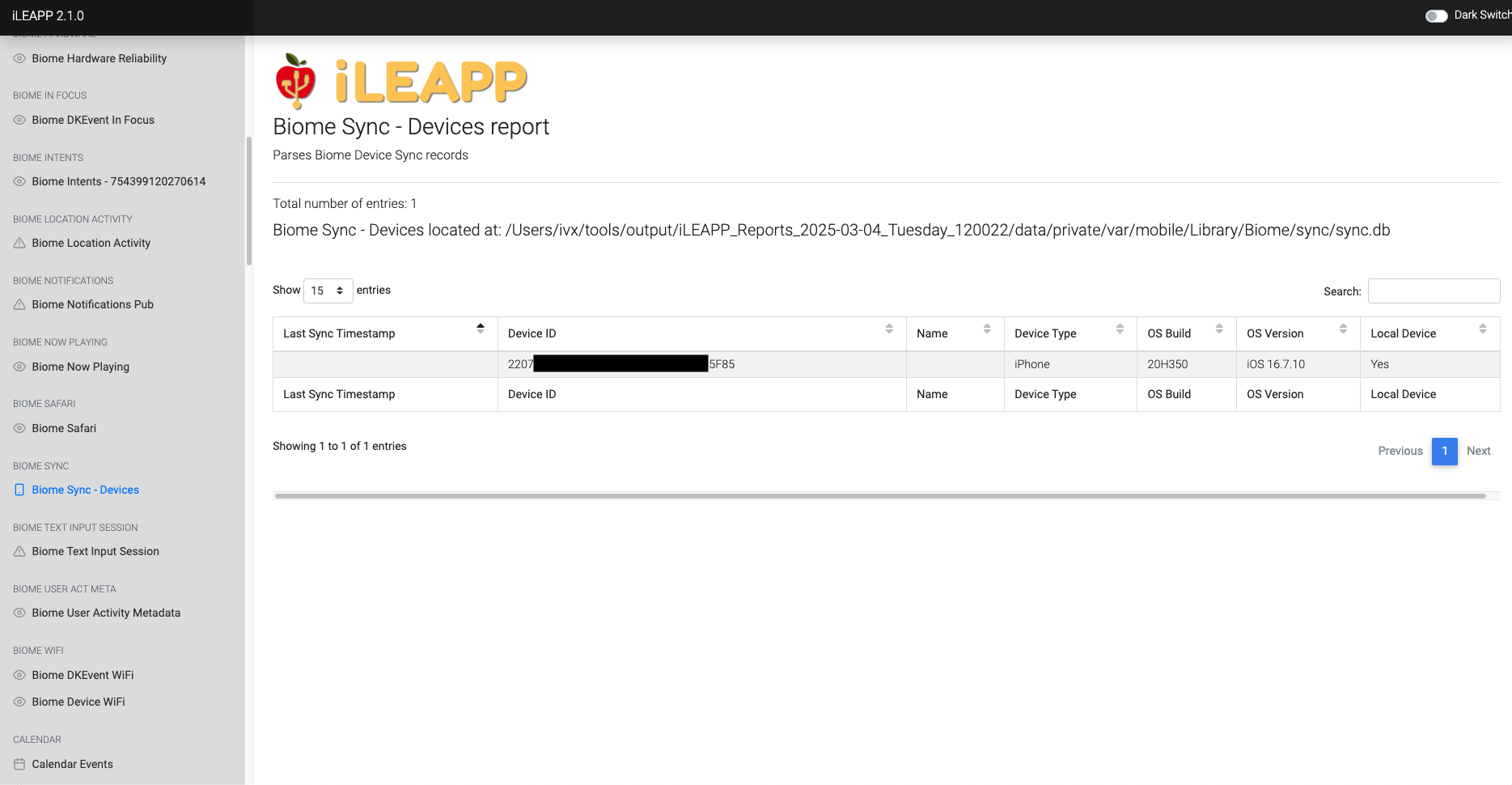
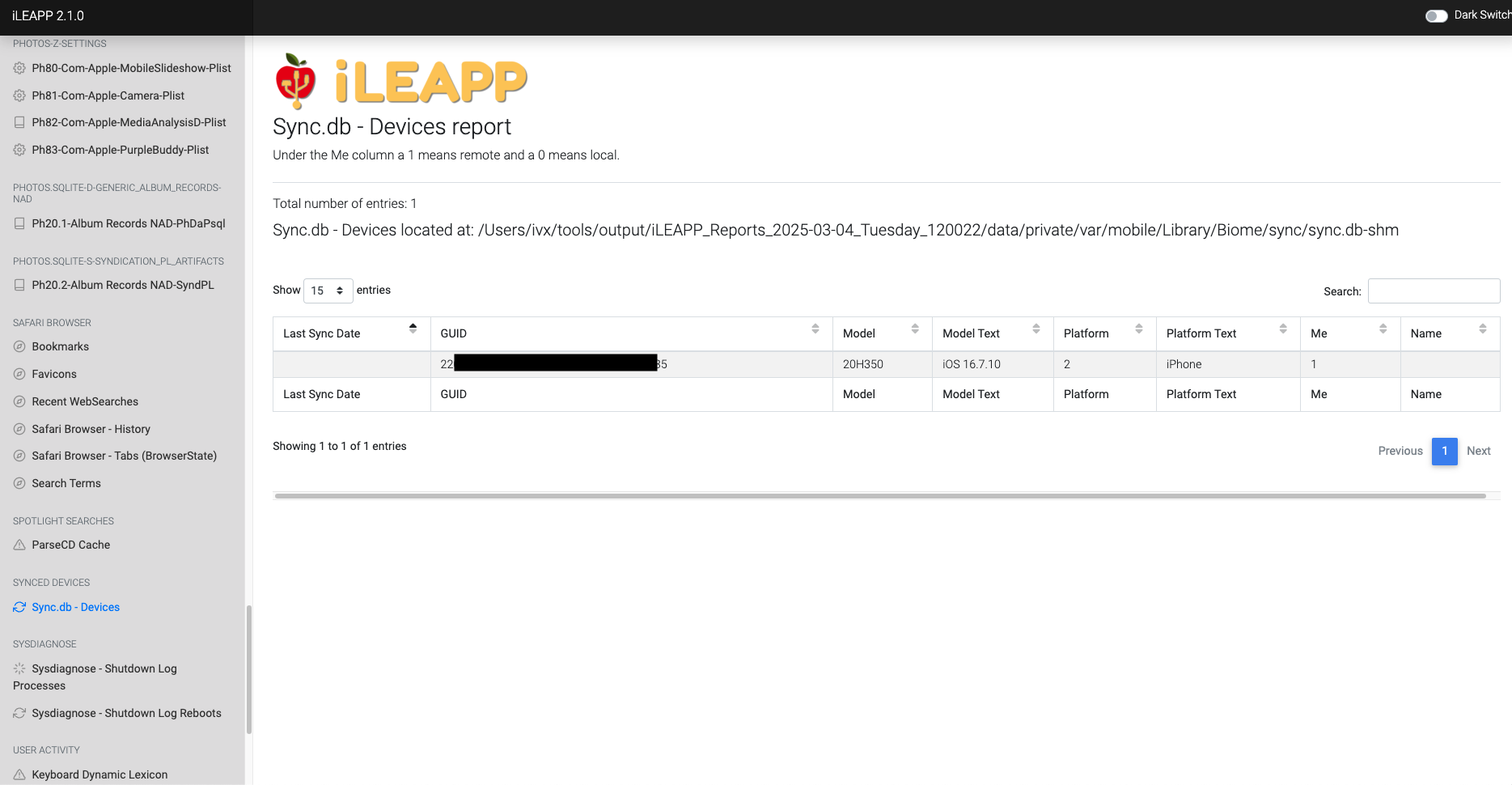
Logs device sync events, tracking connected Apple ecosystem devices.
Records details about text input activity, including typing patterns and sessions.
Stores metadata related to user activities, including interactions with apps and features.
Logs events related to WiFi connections, including network changes and disconnections.
Tracks WiFi-related activities, such as connected networks and signal strength.
Contains details about scheduled calendar events, including dates, times, and locations.
Stores information about available calendars and their associated settings.
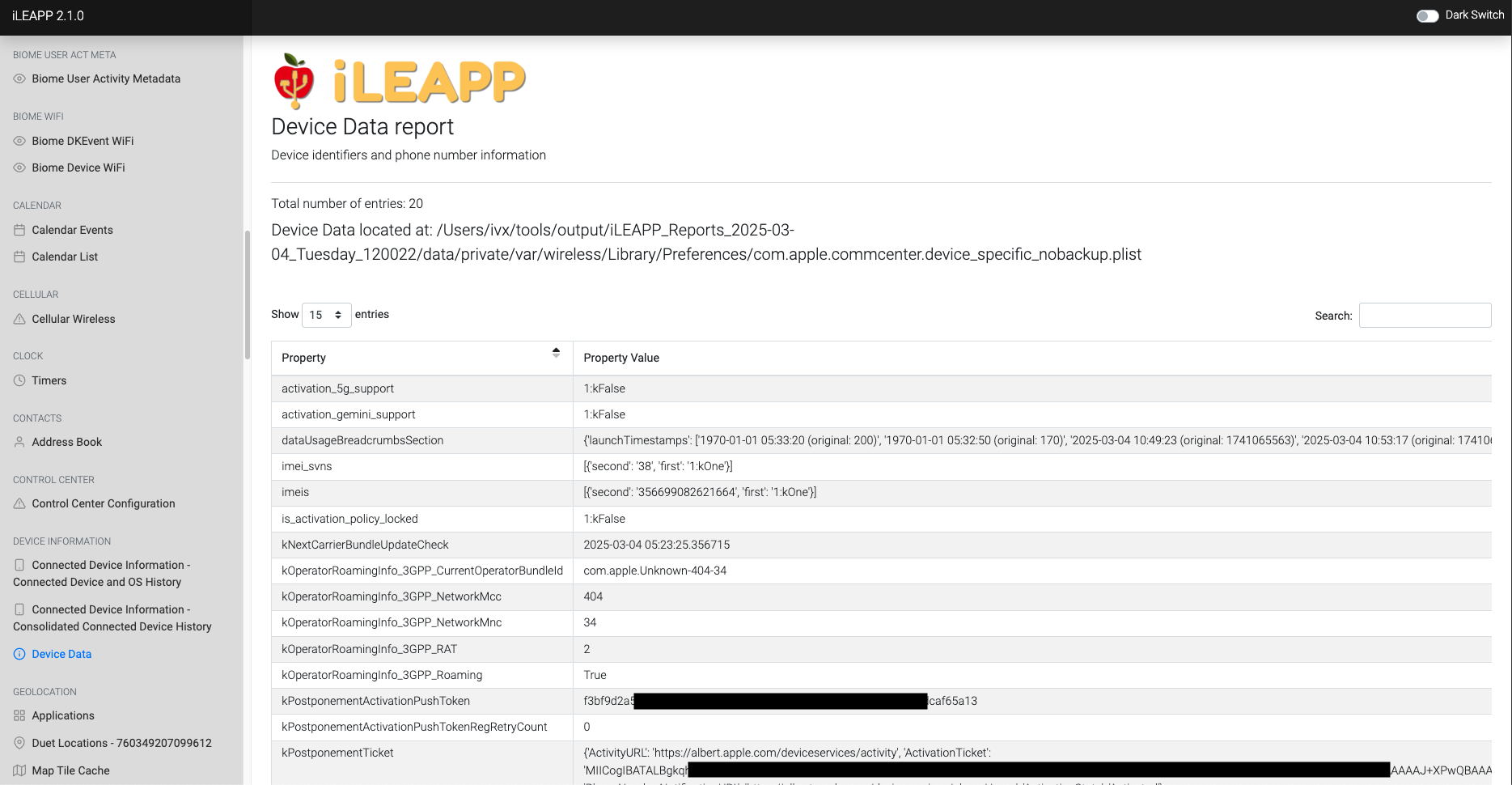
Logs details about cellular network usage, signal strength, and carrier information.
Records information related to system and user-defined timers, such as alarms.
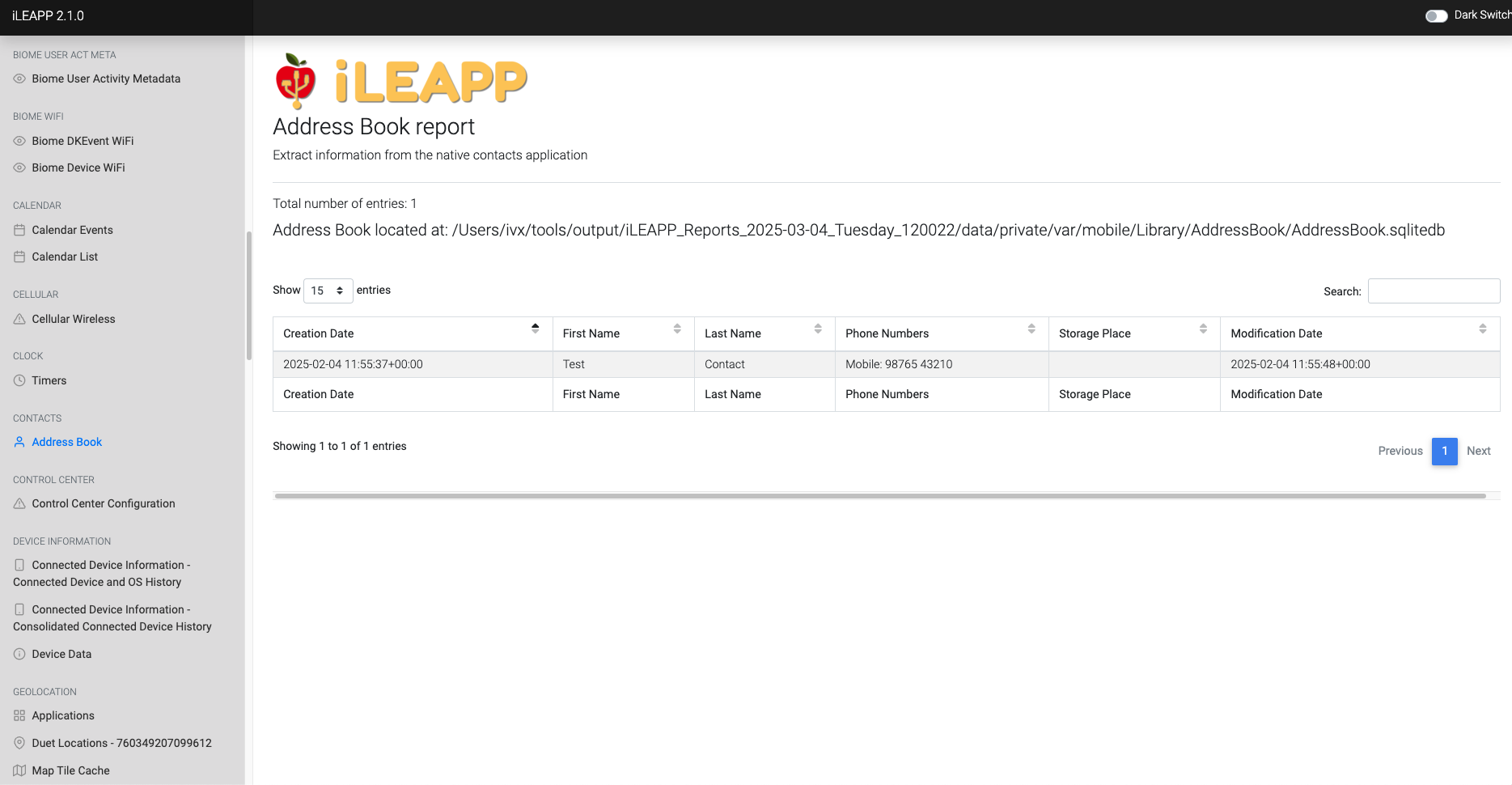
Contains contact details, including names, phone numbers, emails, and addresses.
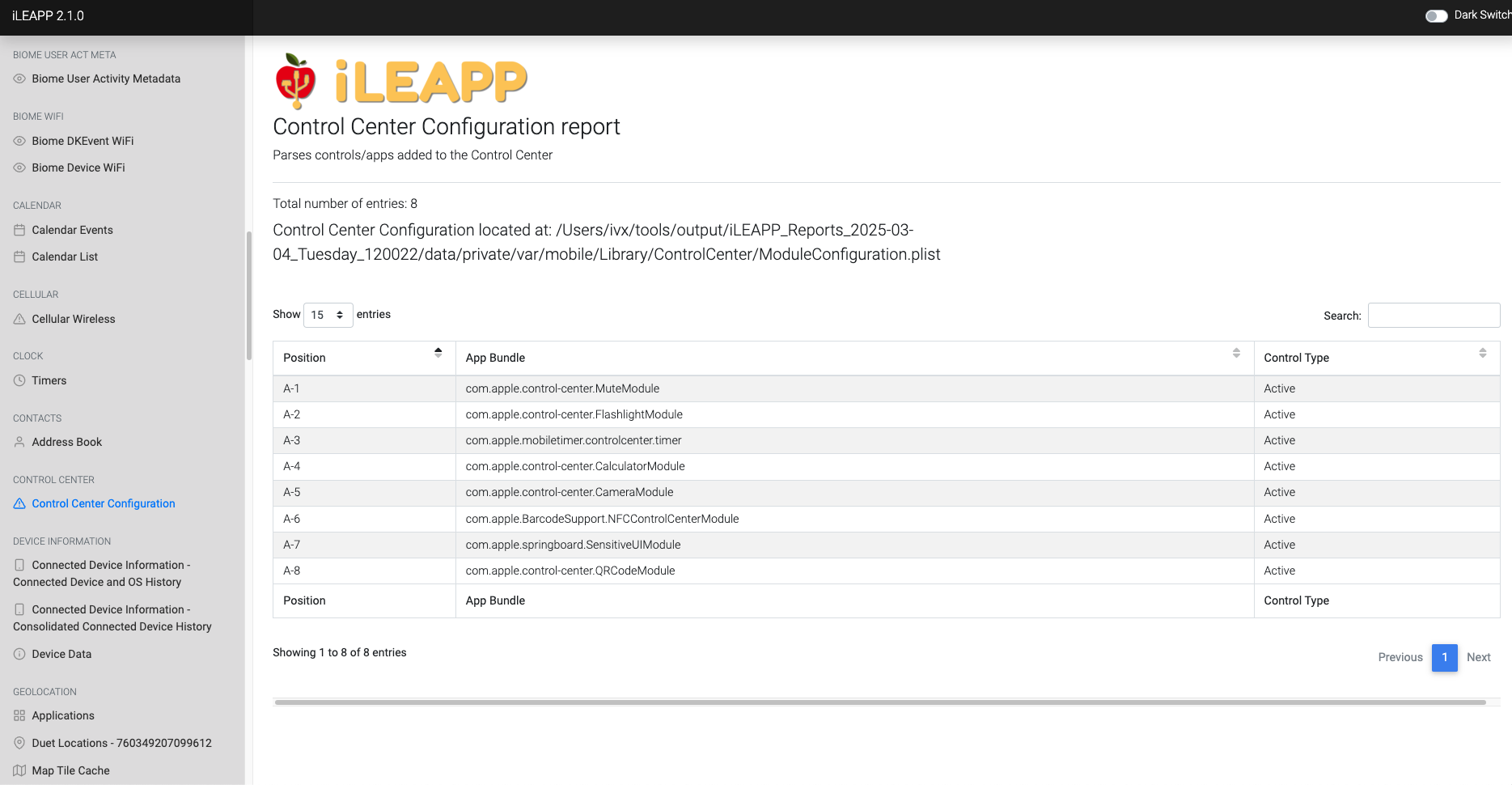
Stores user preferences and settings for the Control Center layout and toggles.
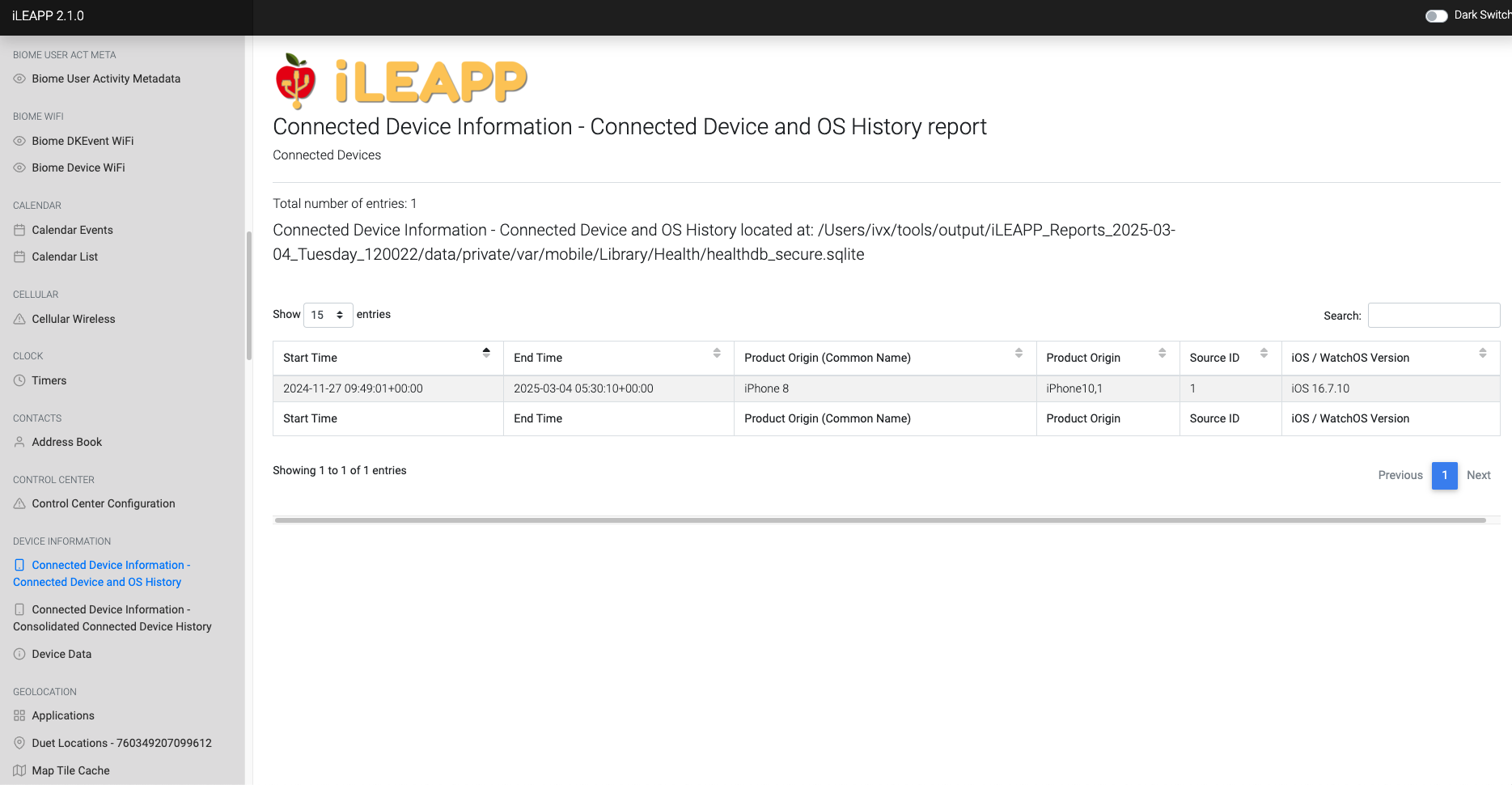
Tracks history of connected devices and their respective operating system versions.
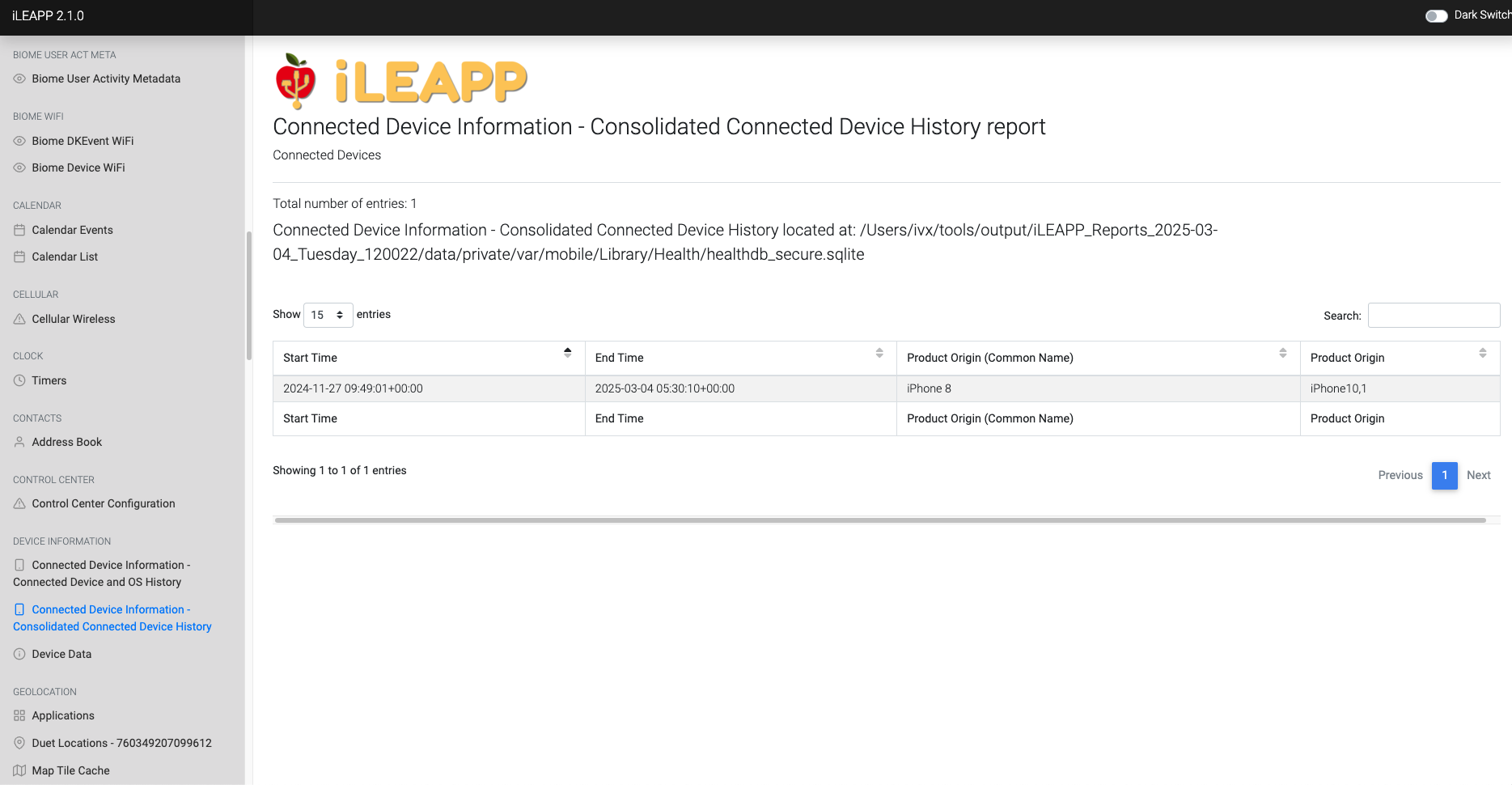
Maintains a comprehensive record of all previously connected devices.
Contains general information about the device, such as model, storage, and system details.
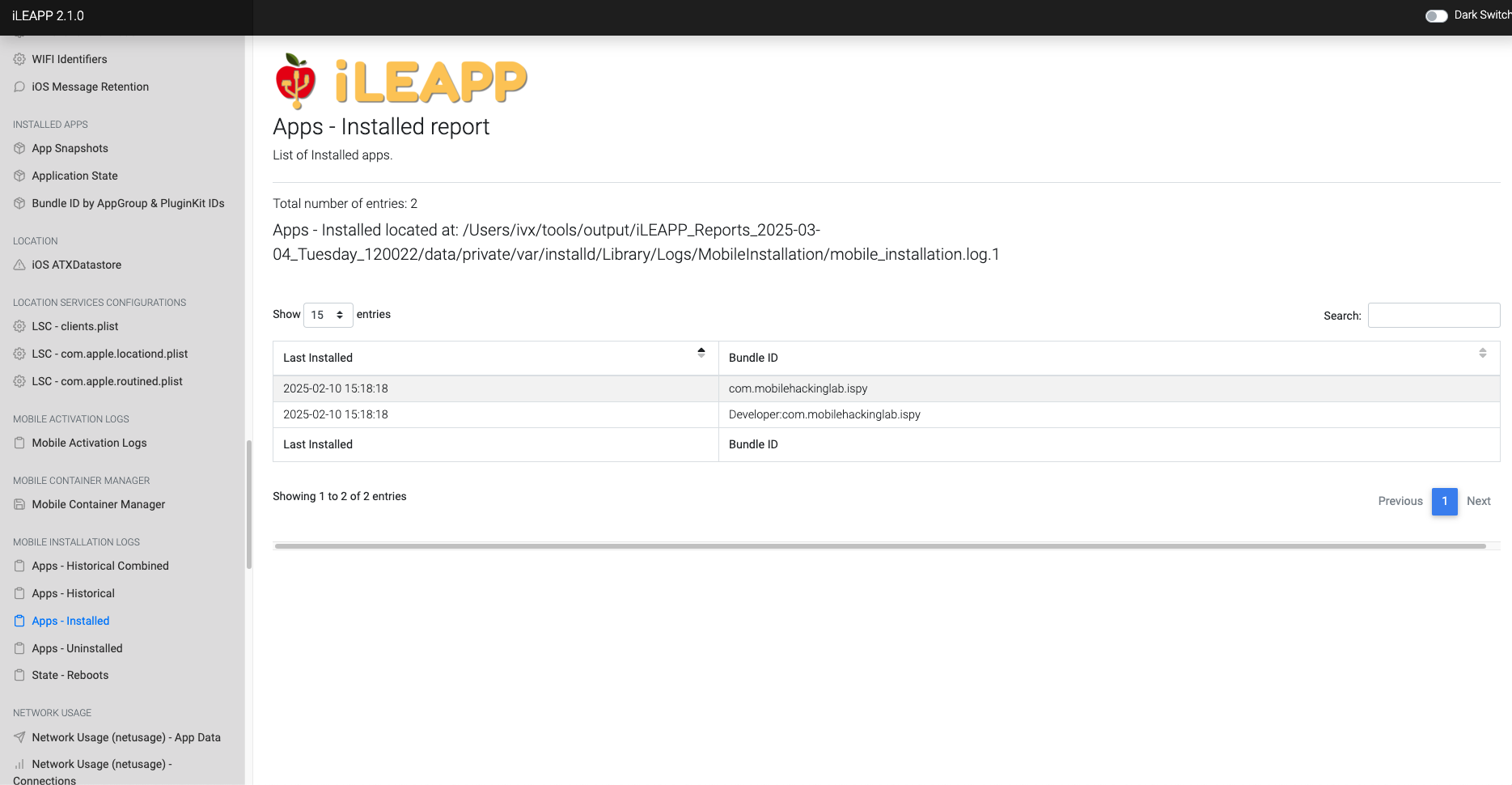
Lists installed applications along with metadata, such as version and developer information.
Tracks location data collected by Apple's Duet framework for contextual awareness.
Stores cached map tiles used in Apple Maps for offline accessibility.
Contains synced map data, including recent locations, searches, and preferences.
Caches location-based data, such as frequently visited places.
Logs sources of health data, detailing how and where health metrics were recorded.
Tracks step count and related movement data collected from the Health app.
Stores details about the operating system version and build information.
Contains general iOS system information, including installed updates and configurations.
Logs backup configurations, including iCloud and local backup settings.
Stores device identifiers such as IMEI (hardware ID) and IMSI (SIM-related ID).
Tracks settings and permissions related to location services on the device.
Records timestamps for system resets, data wipes, or factory resets.
Stores various system and application preference settings in plist format.
Logs timezone settings and changes made by the user or system.
Contains unique identifiers for known WiFi networks the device has connected to.
Stores retention policies and settings for iMessage and SMS history.
Captures previews of apps as they appear when switching between tasks.
Stores the current state of applications, including background activity status.
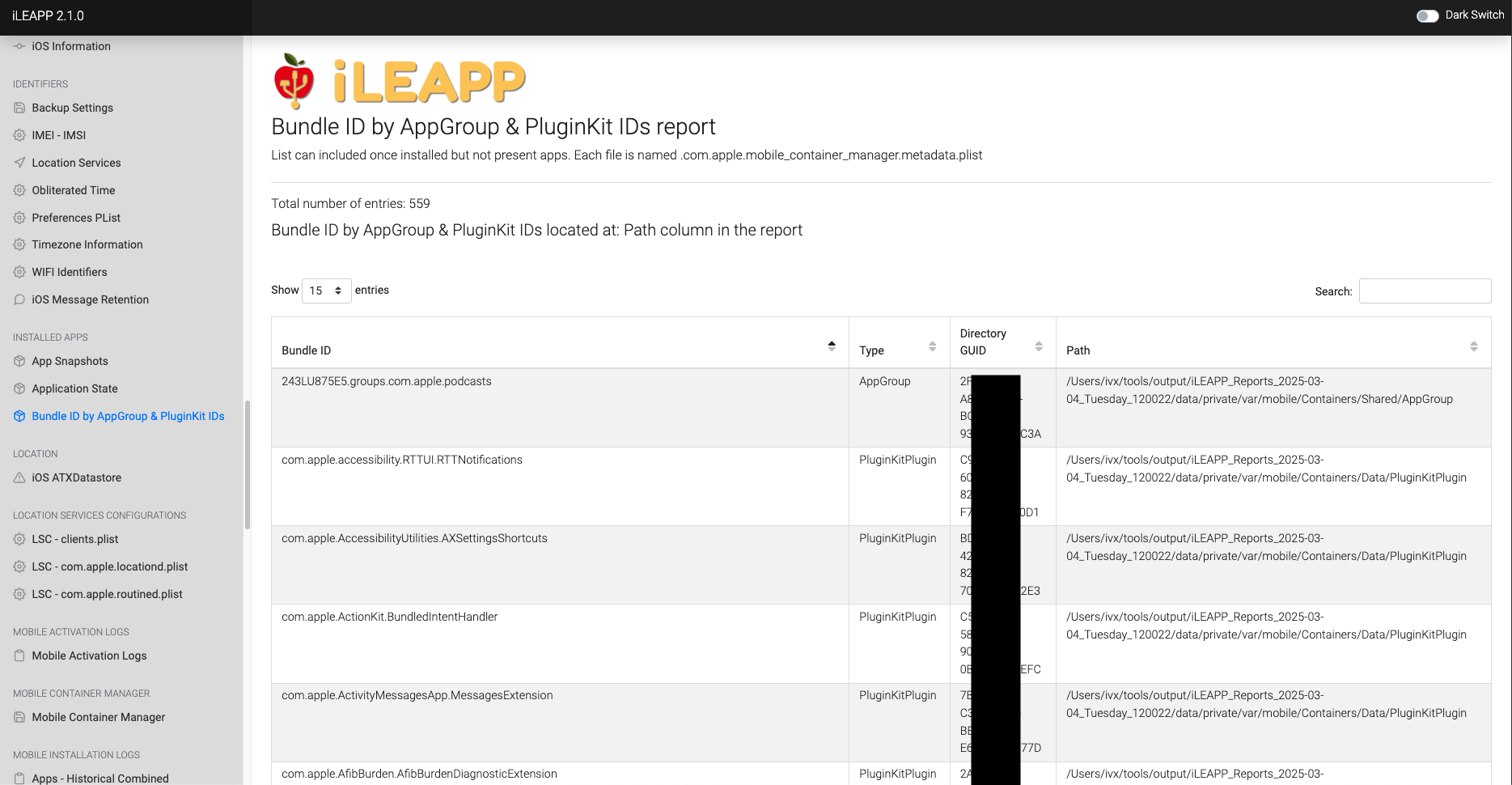
Lists app bundle identifiers associated with AppGroups and PluginKit extensions.
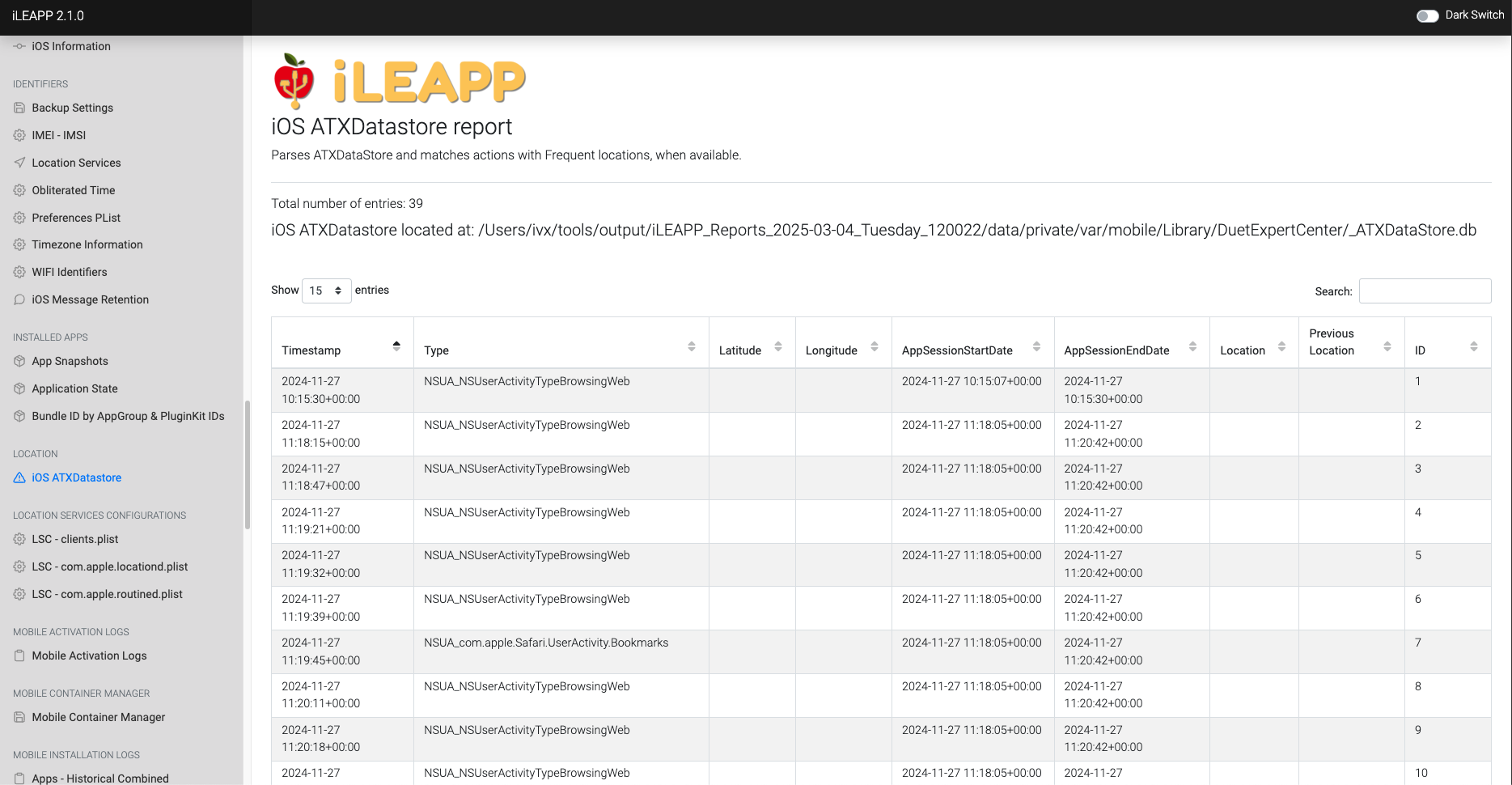
Contains data used by Apple's ATX (App Prediction) framework for app usage analysis.
Stores location service client preferences and history of location access.
Logs system location service settings and permissions granted to apps.
Tracks routine location-based activities used for predictive features.
Contains logs related to device activation and SIM card changes.
Manages app sandbox directories and storage containers on iOS.
Maintains a combined history of installed and removed applications.
Stores historical records of installed applications, including timestamps.
Lists currently installed applications along with their metadata.
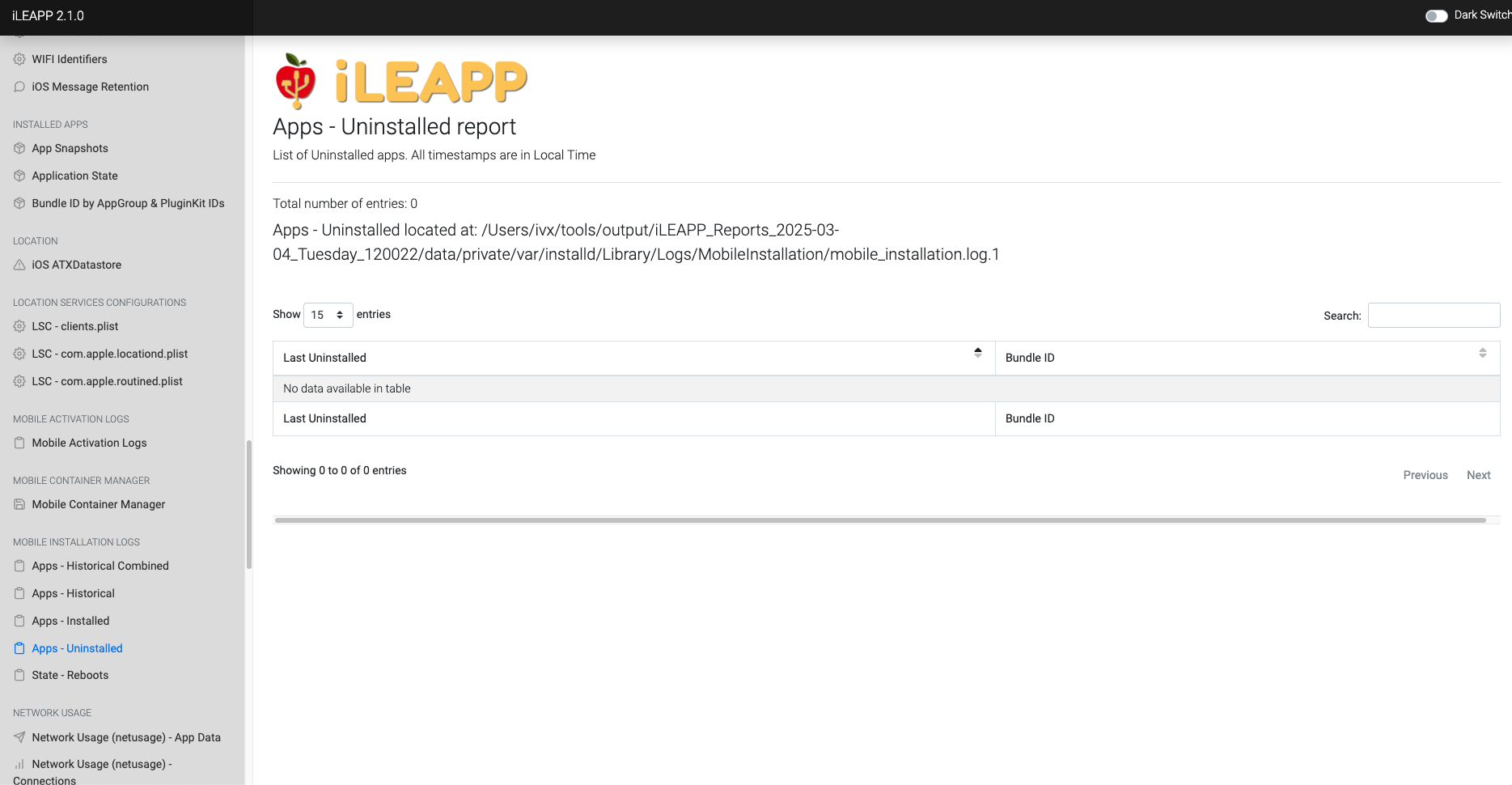
Tracks applications that were previously installed and later removed.
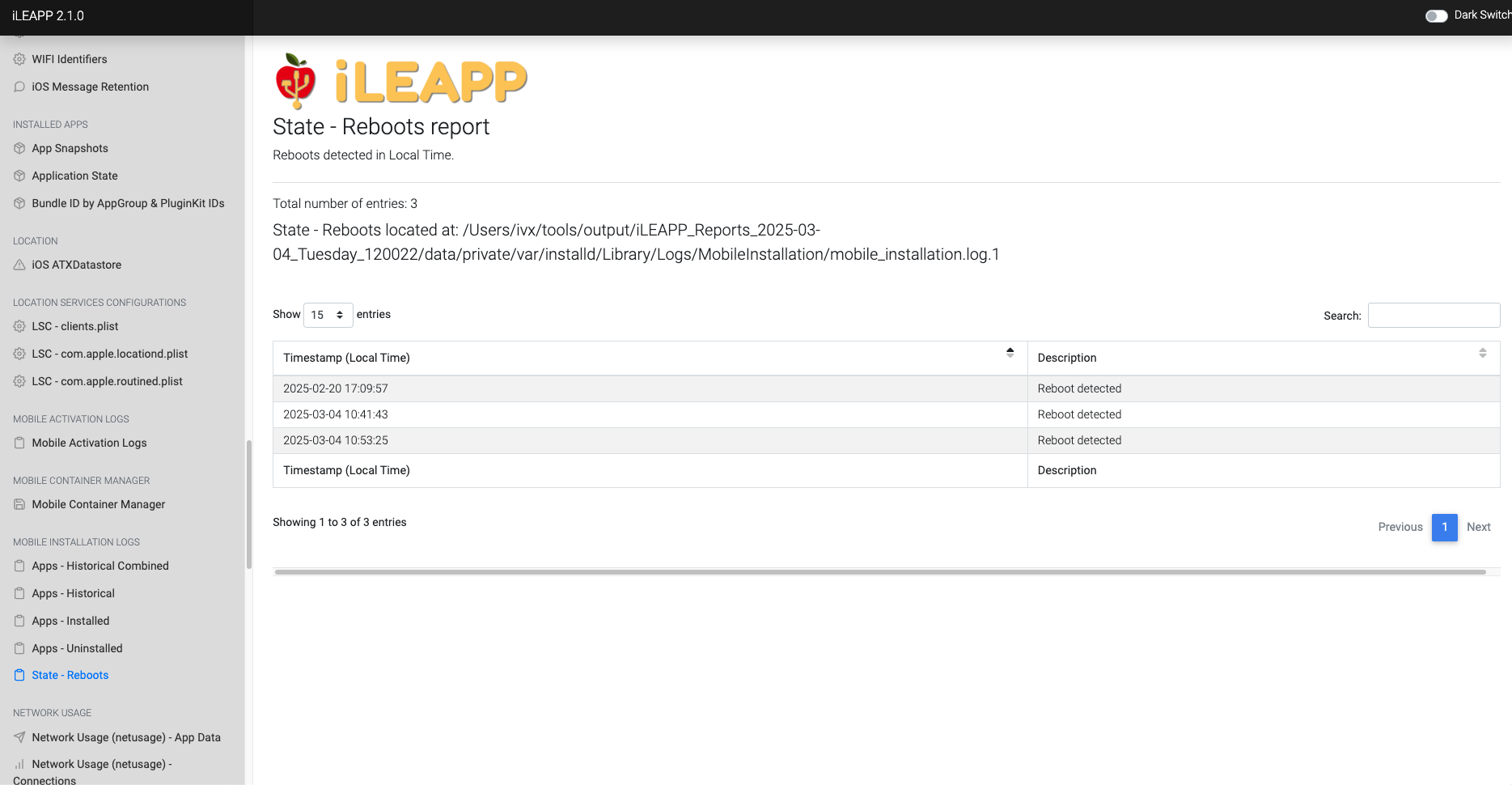
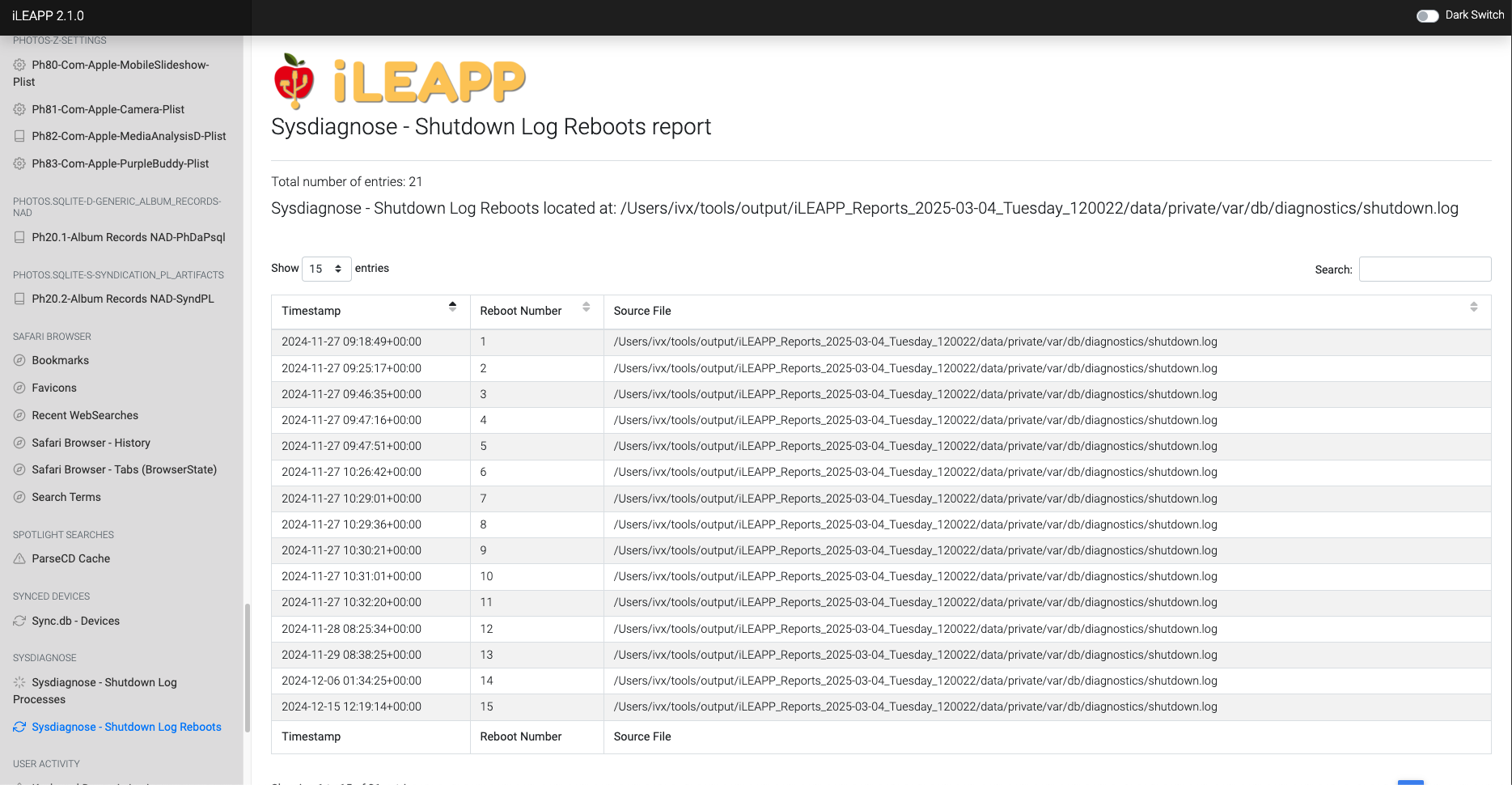
Logs device reboot history, including timestamps and causes.
Records network data usage per app, detailing bytes sent and received.
Tracks network connection events, including IP addresses and timeframes.
Stores notifications processed through Apple's Duet framework for cross-device syncing.
Contains a log of notifications received, including content and timestamps.
Tracks migration-related changes, such as iOS upgrades and data transitions.
Stores settings and metadata related to the Photos app.
Contains configuration details and settings for the Camera app.
Logs data related to media analysis and AI-based categorization.
Tracks data related to the iOS setup assistant and initial device configuration.
Stores structured album record data used in the Photos app database.
Contains album synchronization metadata for shared albums.
Stores saved website bookmarks from Safari and other browsers.
Caches website favicons for faster browser loading.
Logs recent search queries made through Safari and other search interfaces.
Stores browsing history, including visited websites and timestamps.
Tracks open browser tabs and their current state in Safari.
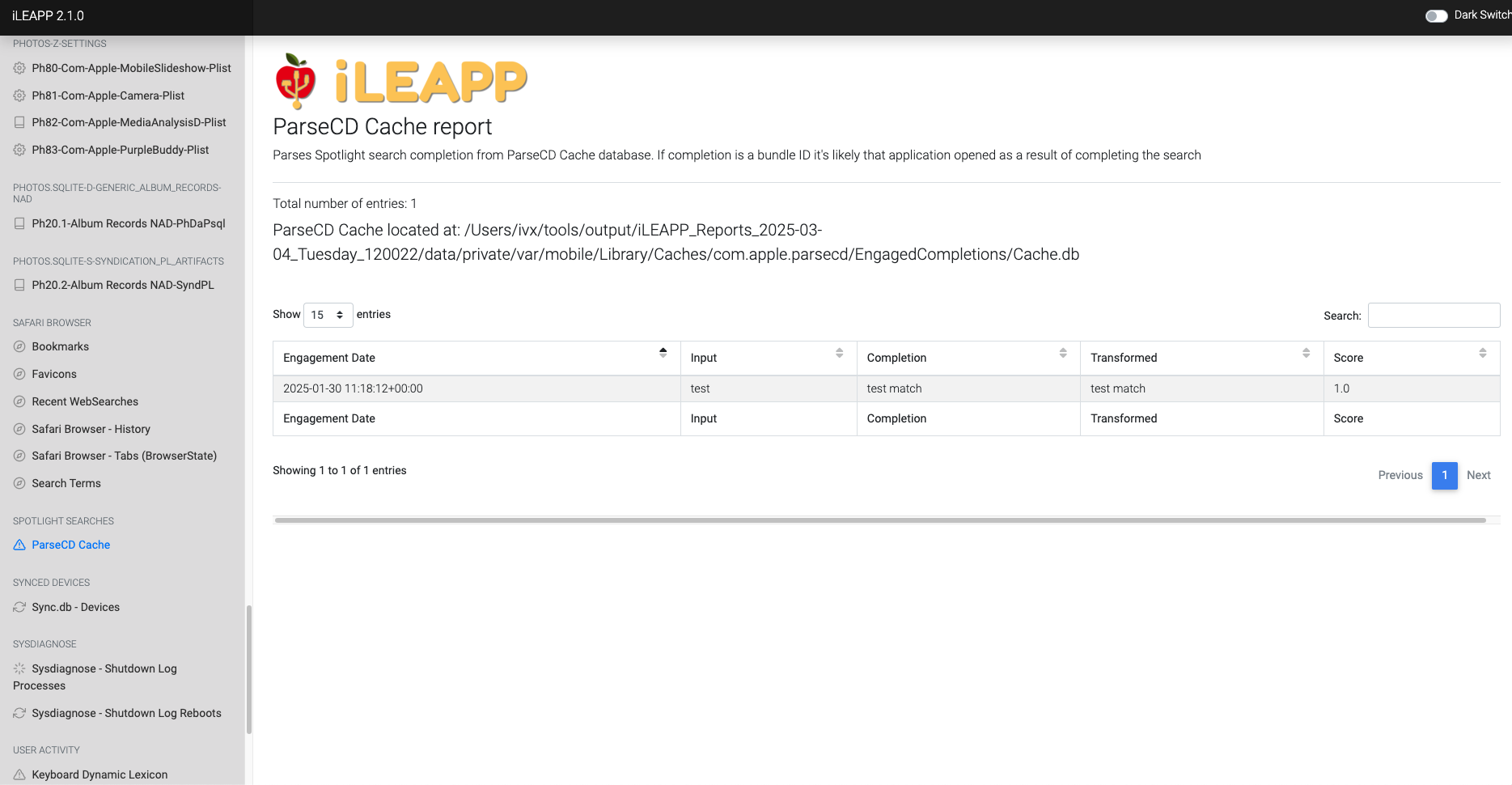
Records search queries entered in various system and app search bars.
Caches parsed content from various sources for faster retrieval.
Stores sync-related data between Apple devices using iCloud or other services.
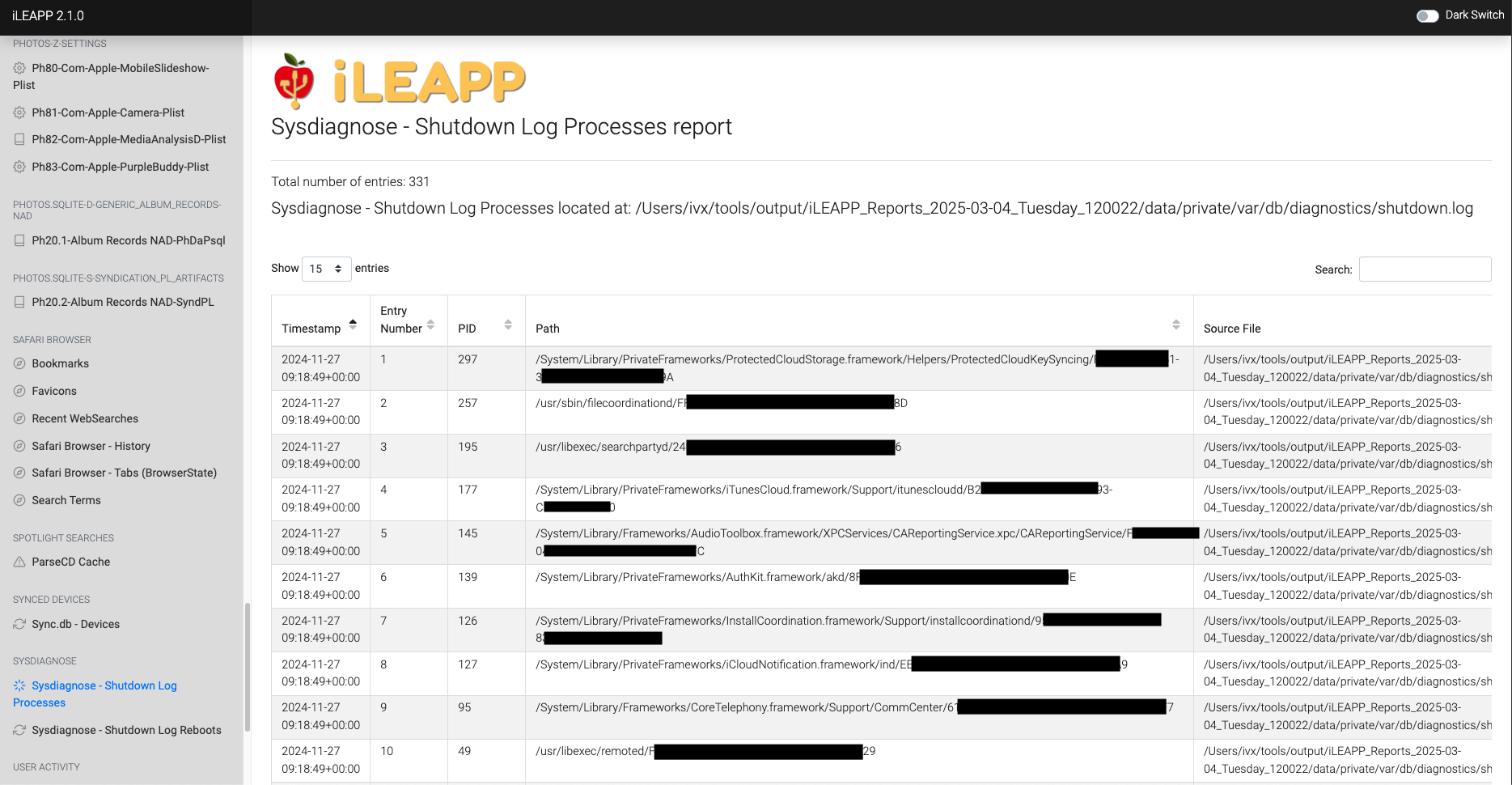
Logs system processes that were running during a device shutdown.
Records details about system reboots, including causes and timestamps.
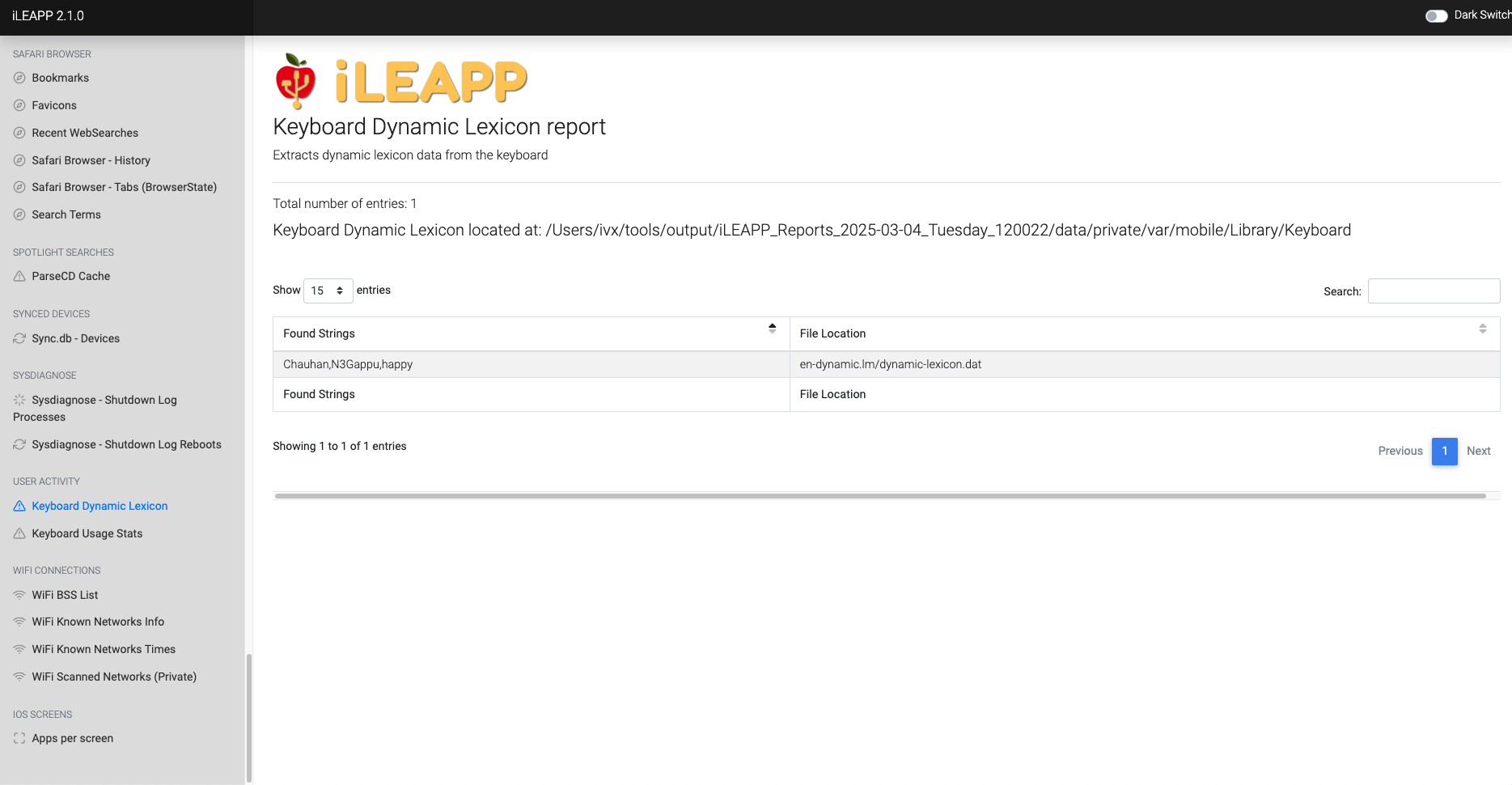
Stores user-specific keyboard predictions and learned words.
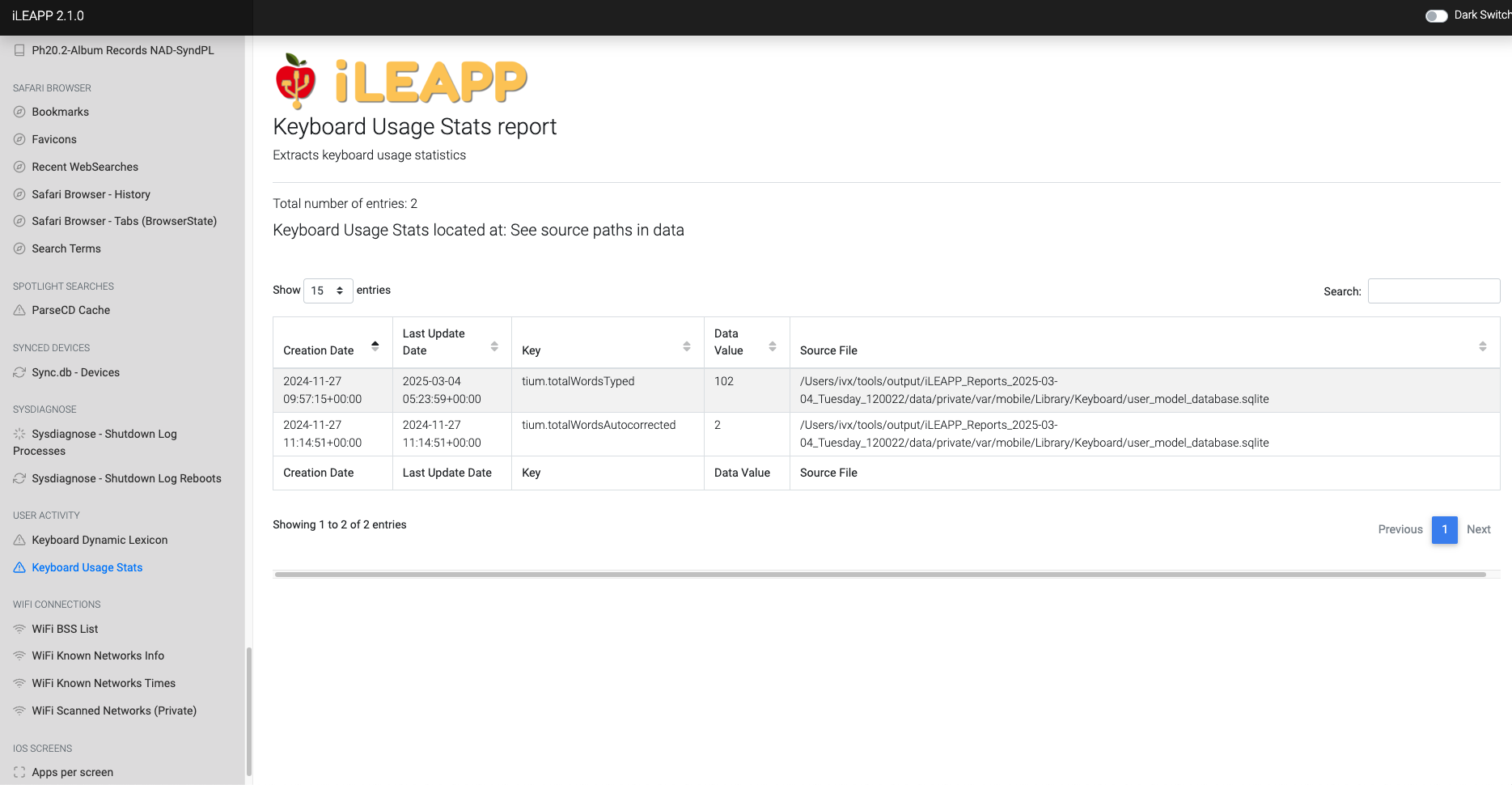
Logs keyboard usage statistics, including frequently used words and phrases.
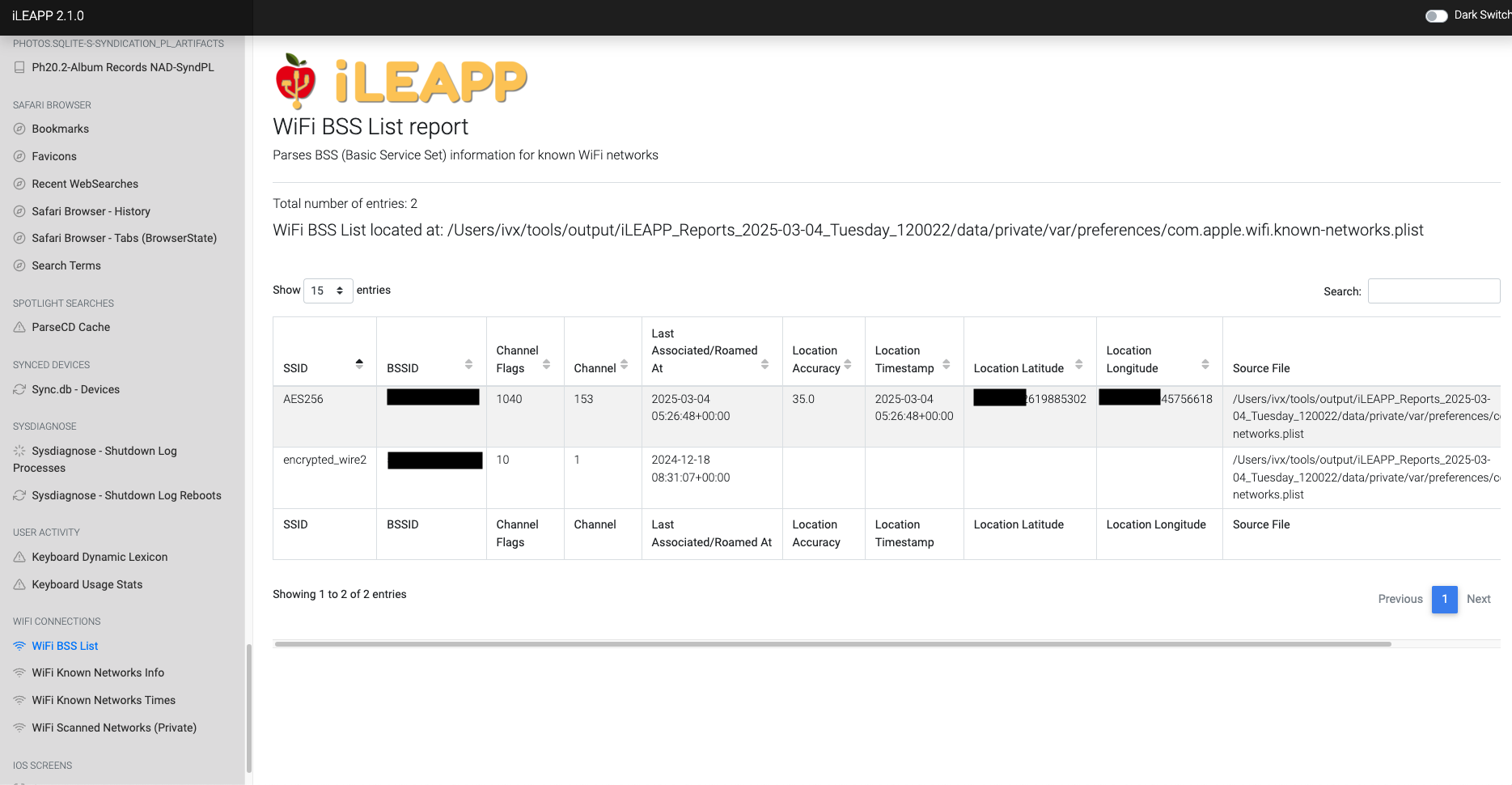
Contains information about nearby WiFi base stations and their details.
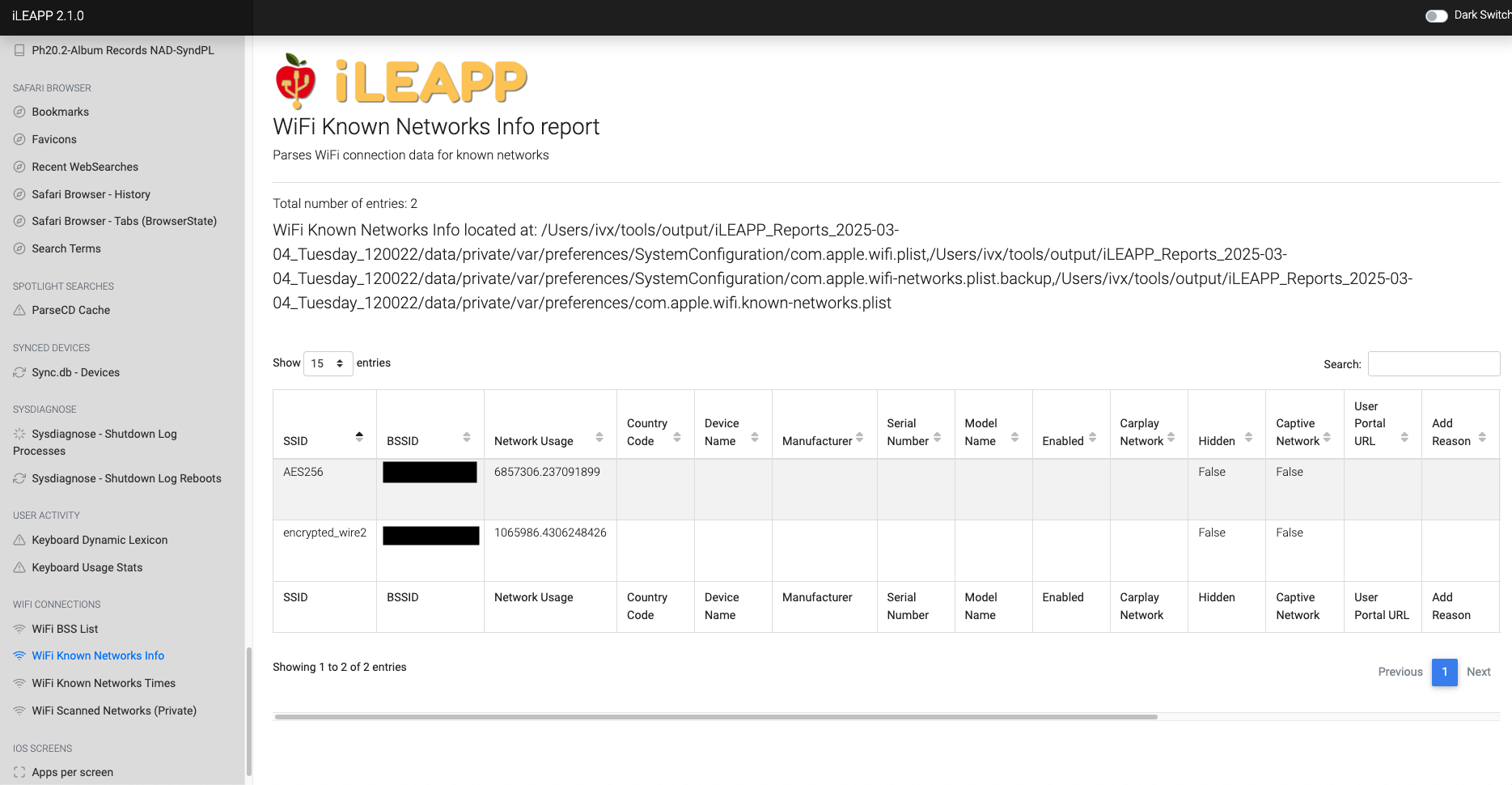
Stores details about known WiFi networks the device has connected to.
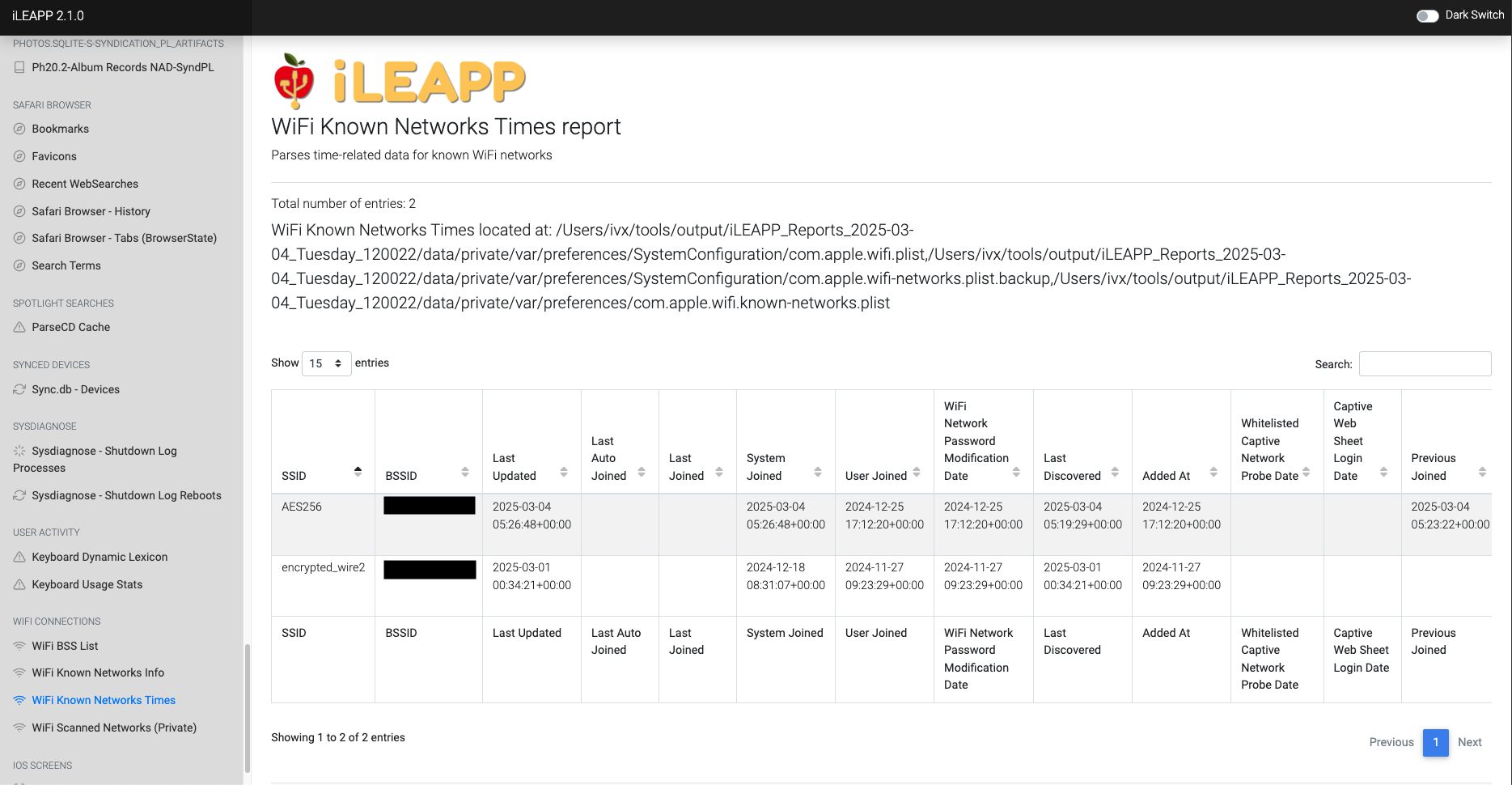
Logs timestamps for past connections to known WiFi networks.
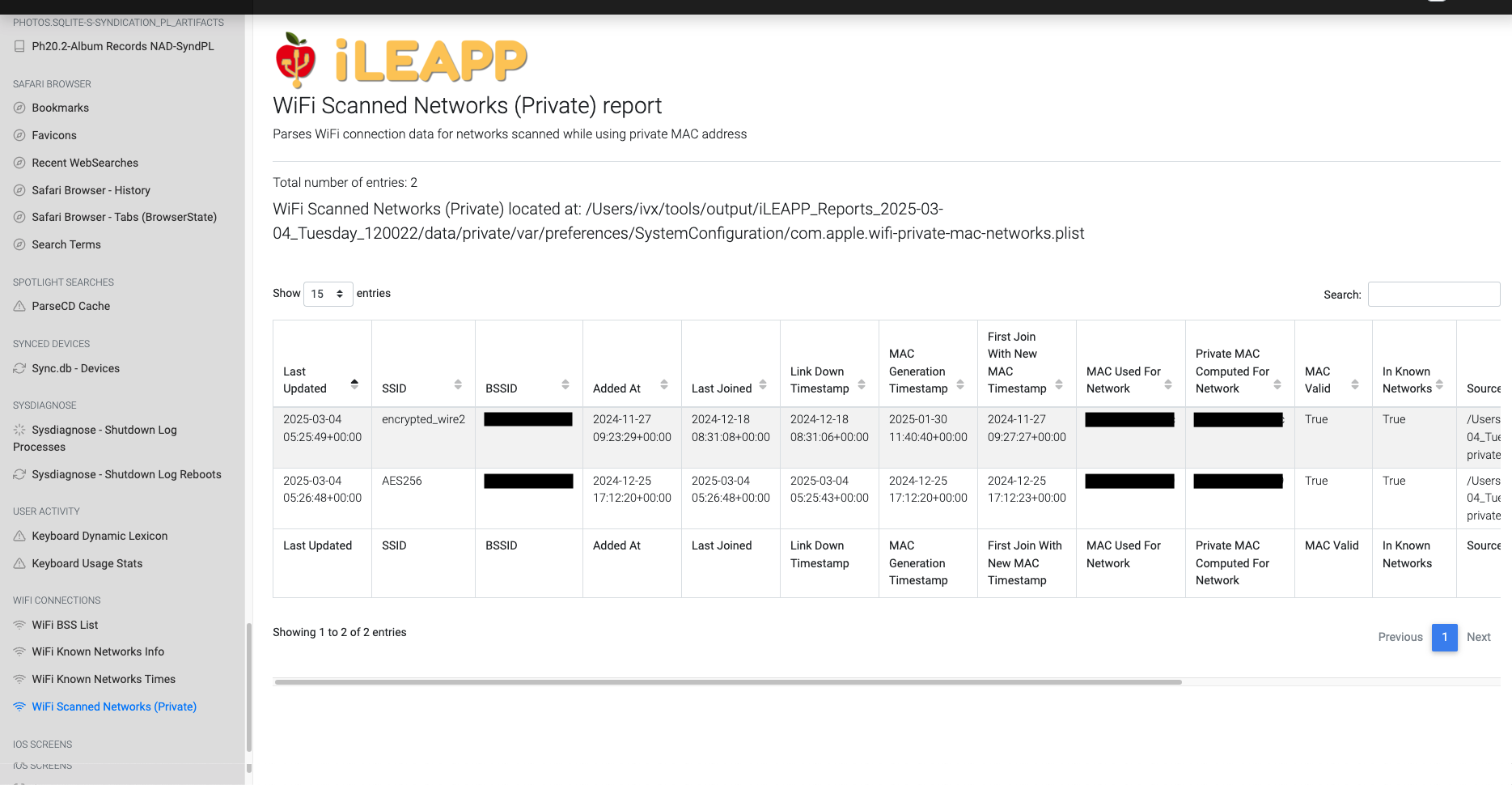
Tracks recently scanned WiFi networks while maintaining user privacy.
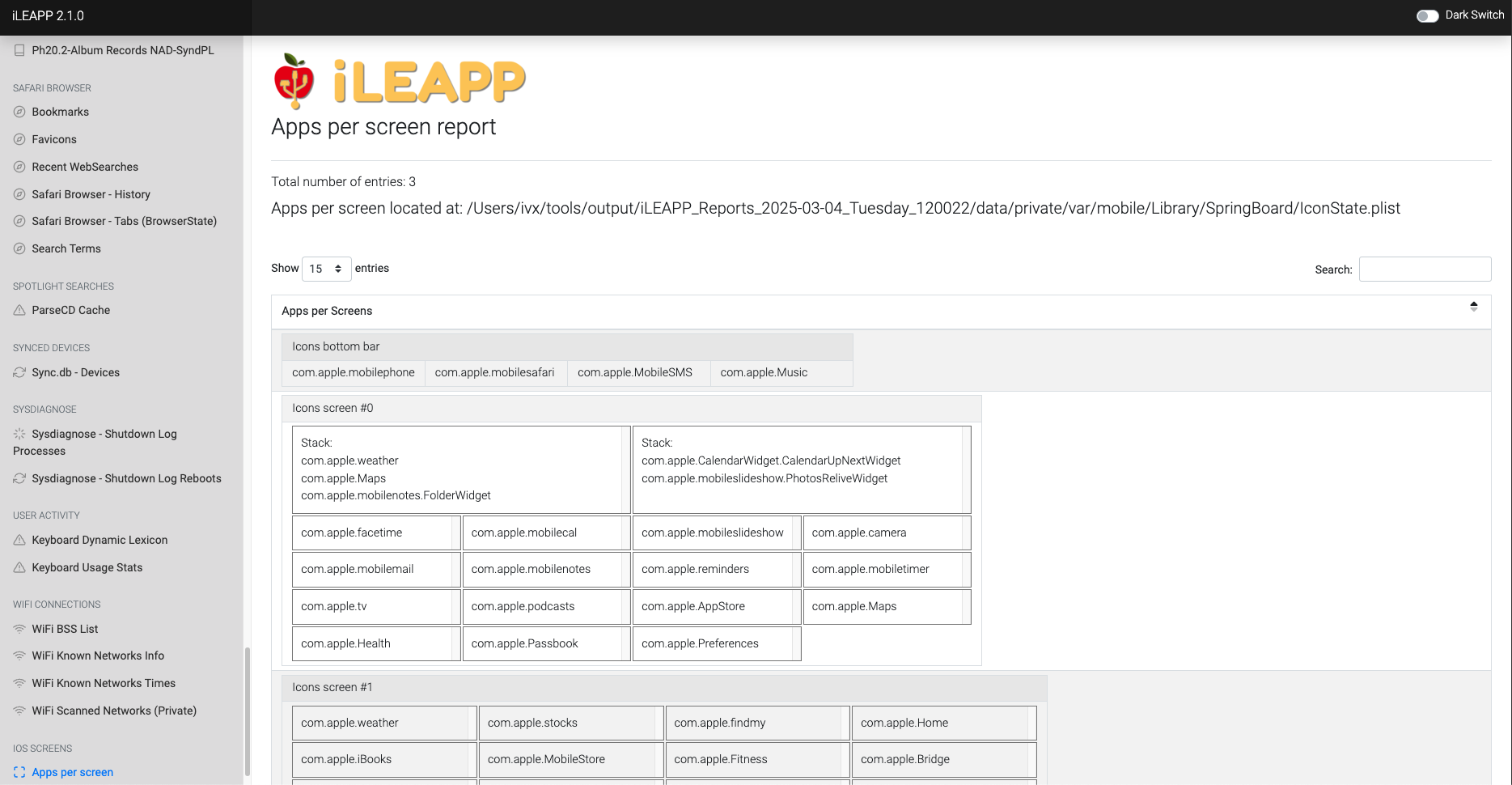
Records the layout of apps across different home screen pages.
iLEAPP is a powerful tool for iOS forensics, offering a wide range of features to extract and analyze data from iOS devices. Its ability to parse logs, events, and plist files provides valuable insights into user activity and system operations. Whether you are conducting digital investigations, incident response, or corporate security assessments, iLEAPP can help you uncover critical evidence and make informed decisions. By following the installation and usage instructions outlined in this article, you can leverage iLEAPP to enhance your iOS forensic capabilities and streamline your investigative processes.